
You might think a colonoscopy or an endoscopy is only for older adults to screen for cancer. But children sometimes have these procedures too to diagnose causes of abdominal pain, chronic diarrhoea, rectal bleeding, and unexplained weight loss. Read on for more about paediatric endoscopy and colonoscopy.
Synopsis
Paediatric Endoscopy and Colonoscopy: Key Procedures
A colonoscopy and endoscopy are common procedures paediatric perform to examine different parts of the digestive tract in children. Colonoscopies focus on the large intestine (colon and rectum), and endoscopies look at the oesophagus, stomach, and the beginning of the small intestine.
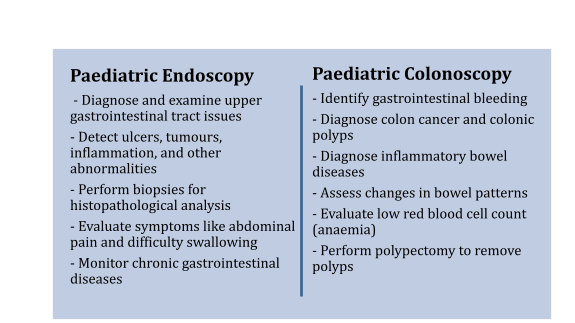
What to Expect: Paediatric Colonoscopy
Before Paediatric Colonoscopy: Two Steps for Good Prep
-
24 Hours Before Your Child's Scheduled Procedure: Only clear liquids should be consumed.
-
Laxatives or Cleansing Solution: Your doctor will provide these before the procedure to clear your child's bowels for optimal visibility during the exam.
During Paediatric Colonoscopy: The Procedure
-
Performing a colonoscopy starts with cleansing the colon. Patients follow a low-fiber or liquid diet to prepare.
-
Throughout the entire procedure, the child needs to stay hydrated.
-
A solution of polyethene glycol and electrolytes is typically administered to patients the day before the colonoscopy to irrigate the bowel. Alternatively, laxative preparations may also be given.
-
Sedatives are often administered intravenously to patients at the beginning of the procedure.
-
To confirm the adequacy of preparation, a digital examination of the rectum is performed first to assess the nature of the sphincter. The anus, rectum, colon, and terminal ileum are then visualised using an endoscope with a movable tip.
-
Also, to visualise abnormalities related to mucosal morphology, a dye is sprayed onto the bowel wall via the endoscope.
-
Suspicious lesions can be treated using laser light or electric wire cuts.
-
Cuts are typically made for biopsies or polypectomy as needed.
-
The entire colonoscopy procedure generally takes approximately 20-30 minutes.
After Paediatric Colonoscopy: What Happens Next?
Discussion of Findings
-
Your paediatric gastroenterologist in Bangalore will discuss the procedure findings with you.
-
They will explain any abnormalities or conditions detected during the colonoscopy.
Biopsy Results
-
The results may take some time if biopsies were taken during the procedure.
-
Your doctor will inform you when the biopsy results are available and discuss their implications.
Post-Sedation Care
-
Your child will require an escort to accompany them home due to the effects of sedation.
-
It's common for children to feel mild discomfort or bloating post-procedure.
-
Passing gas usually helps relieve these symptoms.
Post-Procedure Guidelines
-
Dietary and activity guidelines after the procedure will depend on the specific findings.
-
Your gastroenterologist will provide instructions tailored to your child's condition and recovery needs.
After Paediatric Colonoscopy: What Happens Next?
Discussion of Findings
-
Your paediatric gastroenterologist in Bangalore will discuss the procedure findings with you.
-
They will explain any abnormalities or conditions detected during the colonoscopy.
Biopsy Results
-
The results may take some time if biopsies were taken during the procedure.
-
Your doctor will inform you when the biopsy results are available and discuss their implications.
Post-Sedation Care
-
Your child will require an escort to accompany them home due to the effects of sedation.
-
It's common for children to feel mild discomfort or bloating post-procedure.
-
Passing gas usually helps relieve these symptoms.
Post-Procedure Guidelines
-
Dietary and activity guidelines after the procedure will depend on the specific findings.
-
Your gastroenterologist will provide instructions tailored to your child's condition and recovery needs.
What to Expect: Paediatric Endoscopy
Before Paediatric Upper Endoscopy: EGD Prep Guide
Preparation for a paediatric upper endoscopy (esophagogastroduodenoscopy or EGD) typically involves fasting for a specific period before the procedure. Your child's doctor will provide instructions based on their medical needs and any underlying conditions.
During Paediatric Upper Endoscopy: The Procedure
-
Preparation: Your child will need to fast before the procedure. The care team will provide specific instructions.
-
Procedure: An IV line will be placed to administer sedative medication, making your child sleepy and relaxed. Numbing medicine will be sprayed in the mouth for comfort.
-
Monitoring: A heart and oxygen monitor will monitor your child throughout the procedure.
-
Duration: The test typically lasts about 30 minutes.
Capsule Endoscopy Details
-
Preparation: Measurements of waist, height, and weight will be taken. Eight stickers will be placed on your child's abdomen, connected to a recording device.
-
Procedure: Your child will swallow a small capsule with water. A recorder and battery pack will be secured around their waist.
-
Recording: The recorder captures images over about eight hours, which are later reviewed by an experienced gastroenterologist using a computer program.
After Paediatric Endoscopy: Heading Home
-
A nurse will continue monitoring their recovery, which will involve checking blood pressure, pulse, and oxygen levels regularly.
-
Gradually, as your child recovers, they will be advised to release any ‘wind’ trapped in their large bowel. We understand this can be embarrassing, but it is important for them to ‘let it go.’
-
Your child will eventually be able to sit up and will be offered a drink.
-
Please take care. Initially, your child may feel dizzy and disoriented when getting off the examination trolley. As the effects of the throat spray wear off, they may experience a sore throat.
Activity Restrictions
-
Avoid activities like gymnastics, bicycling, or driving requiring balance or judgment for at least 24 hours.
-
Resume normal activities, eating, and drinking as tolerated once home.
-
Encourage plenty of liquids for hydration.
Conclusion
Endoscopies and colonoscopies are procedures to help doctors see inside your child's body without the need for traditional surgery. These minimally invasive procedures can also be used to collect tissue samples for biopsies and perform small surgical operations.
FAQ's
Take your child to see a doctor if they have any of the following after their colonoscopy:
-
More than three vomits
-
If you see more than half a teaspoon of bright red blood in their poo or vomit
-
Severe tummy pain
-
Severe bloating
-
Fever (temperature over 38 degrees Celsius)
-
They appear unwell or find it difficult to settle
-
If you have any concerns, you should contact the hospital or take them to see a doctor.
The following symptoms in a child may indicate the need for an endoscopy:
-
Chronic abdominal pain
-
Persistent vomiting
-
Difficulty swallowing
A child undergoes a colonoscopy:
-
Presence of blood in stool
-
Chronic diarrhoea or constipation
-
Suspected inflammatory bowel disease



















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read


















