A brain aneurysm is a weak area in the wall of the brain artery that is at risk of rupture. Although most aneurysms are small and do not cause any major issues, a ruptured brain aneurysm can be life-threatening. Around 500,000 brain aneurysm deaths are reported worldwide each year, and half the victims are younger than 50.1 Understanding the causes and symptoms of this brain aneurysm disease helps provide timely intervention and avoid the risk of aneurysm rupture.
Synopsis
Understanding Brain Aneurysms
A brain aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm, occurs when a weakened area of an artery in the brain bulges outward. This weakness in the artery wall, typically due to a lack of muscle or structural integrity, forms a small pocket that fills with blood. As blood flows through the artery, the bulge can expand, increasing pressure on the fragile vessel. Over time, this pressure can cause the aneurysm to rupture, leading to potentially life-threatening complications.
Brain aneurysms most commonly develop in the arteries at the base of the brain, although they can occur in any artery within the brain. It is also common for individuals to have multiple aneurysms. When an aneurysm ruptures, blood leaks into the surrounding brain tissue, increasing pressure and causing swelling. This rupture leads to a subarachnoid haemorrhage, a type of hemorrhagic stroke, which can result in severe complications such as permanent brain damage. Additional risks include vasospasm, hydrocephalus, seizures, coma, or even death.
Signs and Symptoms of a Brain Aneurysm
Most brain aneurysms are small and do not cause any symptoms until they become large and rupture. Some brain aneurysm symptoms may occur due to blood leaks or from pressing the nearby structures.
Symptoms of a brain aneurysm that has not ruptured
-
Headache (very rare if not ruptured)
-
Vision changes
-
Eye pain or inability to move the eye
-
Dilated pupil
-
Numbness or tingling in the head or the face
-
Seizures
When a small amount of blood leaks from the aneurysm, it causes sentinel headaches (warning headaches), which appear days or weeks before significant rupture.
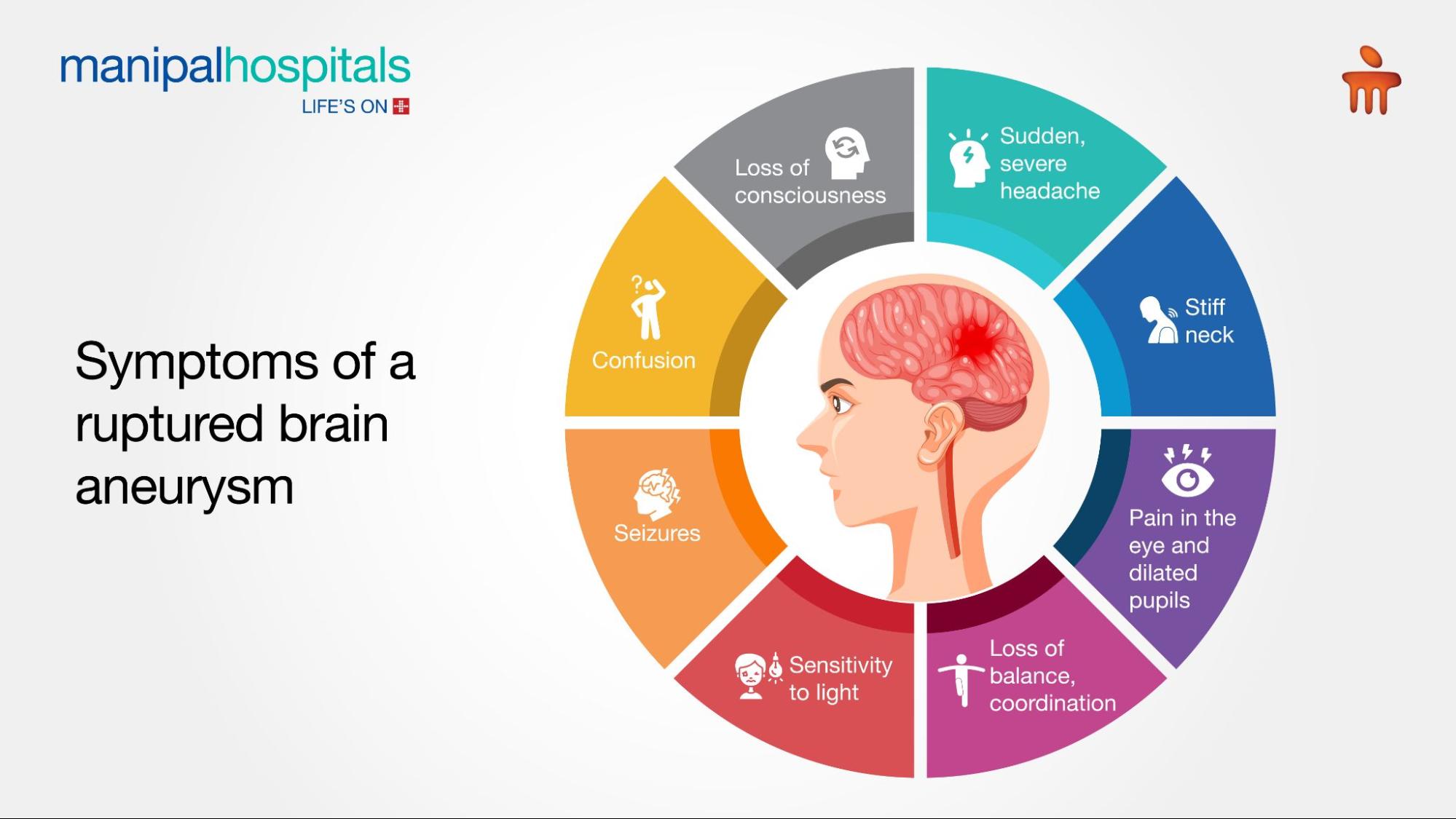
Symptoms of a ruptured brain aneurysm
-
Sudden, severe headache (thunderclap headache)
-
Stiff neck
-
Pain in the eye
-
Drowsiness or loss of consciousness
-
Dilated pupils or drooping eyelid
-
Loss of balance and coordination
-
Back or leg pain
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Blurred or double vision
-
Seizures
-
Confusion
-
Weakness or numbness
A ruptured brain aneurysm requires immediate medical attention. As more time passes without treating the ruptured aneurysm, the chances of death or disability increase.
Causes of Brain Aneurysm
Brain aneurysms develop in arteries that are thin and weak, mostly at the branching point of arteries. In some cases, it develops as a birth defect due to an abnormality in the arterial wall. Those with genetic conditions like Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, or polycystic kidney disease, or those with a family history, also develop brain aneurysms.
A brain aneurysm is more likely to occur in women or individuals between the ages of 30 and 60 years. Those who smoke, have high blood pressure, indulge in substance abuse, or consume excess alcohol are also at higher risk for developing brain aneurysms.
Consult our neurologist in Mukundapur if you need to know more about Brain Aneurysm causes.
Brain Aneurysm Treatment
The treatment for brain aneurysm is primarily focused on reducing or stopping the flow of blood to the region. An unruptured brain aneurysm may or may not require any treatment. However, individuals with a leaking or ruptured brain aneurysm require immediate surgical care.
-
Microvascular Clipping: A small metal clip is attached to the base of the skull to prevent the blood from flowing to the region. It helps stop the brain bleeding or prevents the aneurysm from enlarging and subsequent rupture.
-
Endovascular Coiling: A tiny coil is inserted into the aneurysm to change the pattern of blood flow, leading to clot formation, which seals the aneurysm.
-
Flow Diversion Stents: A mesh tube is placed in the part of the blood vessel that contains the aneurysm to divert the blood away from the region.
Those with ruptured brain aneurysms also require treatment with antiseizure medications and calcium channel blockers to prevent complications.
Consult our neurology hospital in Mukundapur if you need Brain Aneurysm treatment.
Brain Aneurysm Prevention
Although it is not possible to prevent the development of a brain aneurysm, you can reduce your risk by following these measures:
-
Maintain healthy blood pressure (with medication or lifestyle changes)
-
Quit smoking
-
Avoid alcohol or substance abuse
Conclusion
Brain aneurysms cause severe neurological disease symptoms that can be life-threatening. Therefore, it becomes important for individuals with suspicion of brain aneurysms to undergo early detection and timely treatment. If you have symptoms of a brain aneurysm or have risk factors for the disease, visit Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, for comprehensive treatment and guidance.
FAQ's
Some cases of brain aneurysm are diagnosed with symptoms, but not everyone exhibits them. Diagnostic scans like CT scans or MRIs can help visualise the aneurysm, but some patients may have to undergo Angiography to get a clearer view of the blood vessels and the arteries. A spinal tap may be performed in individuals with a slight bleed from the aneurysm.
You need to undergo a screening test:
-
If you have suffered from a brain aneurysm in the past
-
If you have developed subarachnoid haemorrhage
-
If you have a family history of cerebral aneurysm
-
If you have a genetic condition that could lead to a brain aneurysm
Some brain aneurysms do not rupture or may even shrink over time, not leading to any long-term complications. However, getting evaluated by a healthcare professional is essential to prevent any unpleasant complications.
The prognosis depends on the age, health status, aneurysm location, and extent of bleeding. Most individuals with ruptured aneurysms do not survive the first 24 hours or die from complications within six months. Therefore, early detection and timely intervention become crucial for optimal aneurysm management.
You can schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, by contacting us or visiting our website.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read