Cardiovascular diseases, especially heart attacks, are silent killers and the leading cause of death worldwide. Around 24.2% of all the deaths in India occur due to cardiovascular diseases. The incidence of heart attacks has increased by over 50%, and nowadays they tend to occur at an early age without any prior warning. A heart attack is an urgent medical situation that needs immediate attention. Knowing how to respond immediately and effectively can save a person’s life. This blog guides you through the basics of heart attacks, recognising the symptoms, and taking the essential, crucial steps when someone is experiencing a heart attack.
Synopsis
What is Heart Attack?
A heart attack, also called myocardial infarction, is a hazardous medical condition in which a blockage in the heart muscles occurs, leading to a deficiency of oxygen-rich blood. If the blockage goes untreated for longer, it damages heart muscles, leading to further complications. There can be various reasons or conditions for this blockage. Usually, the heart attacks are mild, and if given the right treatment immediately, the person can be saved. But an emergency can occur anytime, and every minute is critical, so understanding its symptoms and first aid for a heart attack is crucial.
What are the Symptoms of Heart Attack?
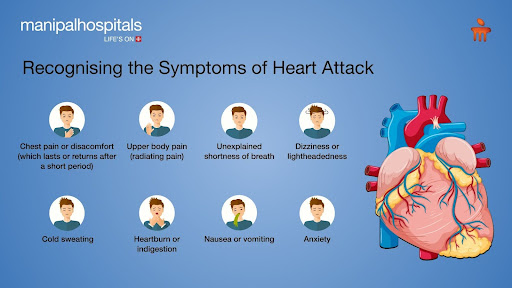
Recognising the early symptoms of heart blockage is crucial for timely intervention in an emergency. These can vary between individuals, with women often experiencing less typical symptoms such as shortness of breath, back or jaw pain, and nausea or vomiting. Common symptoms include:
-
Chest pain or discomfort (which lasts or returns after a short period)
-
Upper body pain (radiating pain)
-
Cold sweating
-
Heartburn or indigestion
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness
If you see any of these symptoms of heart blockage, seek immediate help from a cardiologist at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, for timely intervention and appropriate heart blockage treatment, saving your or your loved one’s lives.
What are the Causes of Heart Attack?
There can be various reasons for a heart attack, such as:
-
Diabetes
-
Atherosclerosis
-
Family history of heart diseases
-
Obesity
-
Certain infections
-
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection
-
Coronary artery spasm
-
Consumption of tobacco and illegal drugs
-
Excessive consumption of alcohol
-
Anxiety and stress
-
Unhealthy lifestyle
How to Act if You Witness Someone Having a Heart Attack?
When you suspect someone is experiencing a heart attack, it's important to act quickly and calmly. The chances of survival after a heart attack are higher if prompt treatment is given. Follow these first-aid tips:
-
Call Emergency Medical Services: Call the emergency services helpline immediately for help. Time is critical, and emergency medical technicians (EMTs) can start treatment in the ambulance on the way to the hospital.
-
Keep the Person Calm and Seated: Assist the person to sit or lie down comfortably and stay calm. Remove any restrictive garments and encourage them to rest.
-
Administer Aspirin: If the person is conscious and not allergic to aspirin, give them a standard dose of aspirin (about 300 mg) to chew slowly. Aspirin helps by thinning the blood and reducing the size of the blood clot, helping in healthy blood flow.
-
Perform CPR if trained: If the person loses consciousness and isn't breathing or doesn't have a pulse, start cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) immediately if you are qualified. Push hard and fast in the centre of the chest at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. Also, provide rescue breathing after every 30 compressions to sustain blood and oxygen flow to the brain and heart.
-
Support and Monitor: Until medical help arrives, be by the patient's side, assuring them they are not alone. Monitor their response and make them take their heart medications (if already prescribed).
Nobody plans a heart attack, but it's crucial to stay prepared to take care of your and your loved one's health in case of an emergency. Never neglect your health; it's better to be safe than sorry.
Conclusion
Being prepared to respond to a heart attack timely can save lives. Recognising the early signs and acting quickly can significantly impact the outcome. Educate yourself and others about these essential steps, and consider taking a CPR and first aid course to be better prepared in emergencies. Book an appointment at our Cardiology Hospital in Mukundapur to map out your ideal treatment.
FAQ's
A heart attack can lead to various complications, including:
-
Cardiogenic shock
-
Heart failure
-
Arrhythmias
-
Pericarditis
-
Cardiac arrest
However, it is important to take immediate treatment for heart blockage to avoid further complications.
Taking certain steps can lower your chances of having a heart attack and can even help after your first heart attack:
-
Exercise regularly
-
Eat a heart-healthy diet
-
Take good sleep
-
Quit smoking and tobacco
-
Stay away from stress
-
Get regular health checkups
-
Take medications timely (as directed by the doctor)
-
Manage other health conditions
The tests used to diagnose a heart attack are:
-
Blood tests (cardiac markers)
-
Chest X-ray
-
Electrocardiogram
-
Echocardiogram
-
Coronary catheterisation (angiogram)
-
Cardiac CT scan
-
Cardiac MRI
Every minute after a heart attack is crucial. Oxygen is given immediately, and heart blockage treatment depends on the type of heart blockage, whether it is a partial or complete blockage. The common treatment options are:
-
Medications (aspirin, clot busters, nitroglycerine, other blood-thinning medicines, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, morphine, statins)
-
Coronary Angioplasty and Stenting
-
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
-
Cardiac Rehabilitation
If you suspect heart blockage, seek consultation with our experienced cardiologist for personalised and effective treatment.
To schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, contact our Cardiology Department or visit our website.



















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read





11.png)











