Listen to article
Loading audio...
What if the body’s immune system, which is normally responsible for protecting the body from foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses, starts destroying its organs and tissues? This happens in lupus, a disease that can affect any part of the body. The prevalence of lupus is increasing in India, with reports indicating it affects 3.2 per 100,000 people. Lupus can be life-threatening, so recognising the signs and symptoms of lupus is crucial for timely intervention and management. This blog will guide you through understanding lupus, its signs and symptoms, and how to identify the condition early.
Synopsis
What is Lupus Disease?
Lupus is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system goes into overdrive, attacking normal cells and tissues, leading to inflammation and damage. Lupus disease is also known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The condition can affect multiple organs throughout your body, such as the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, heart, and lungs, making it a complex disease to diagnose and manage.
How to Recognise Early Signs and Symptoms of Lupus?
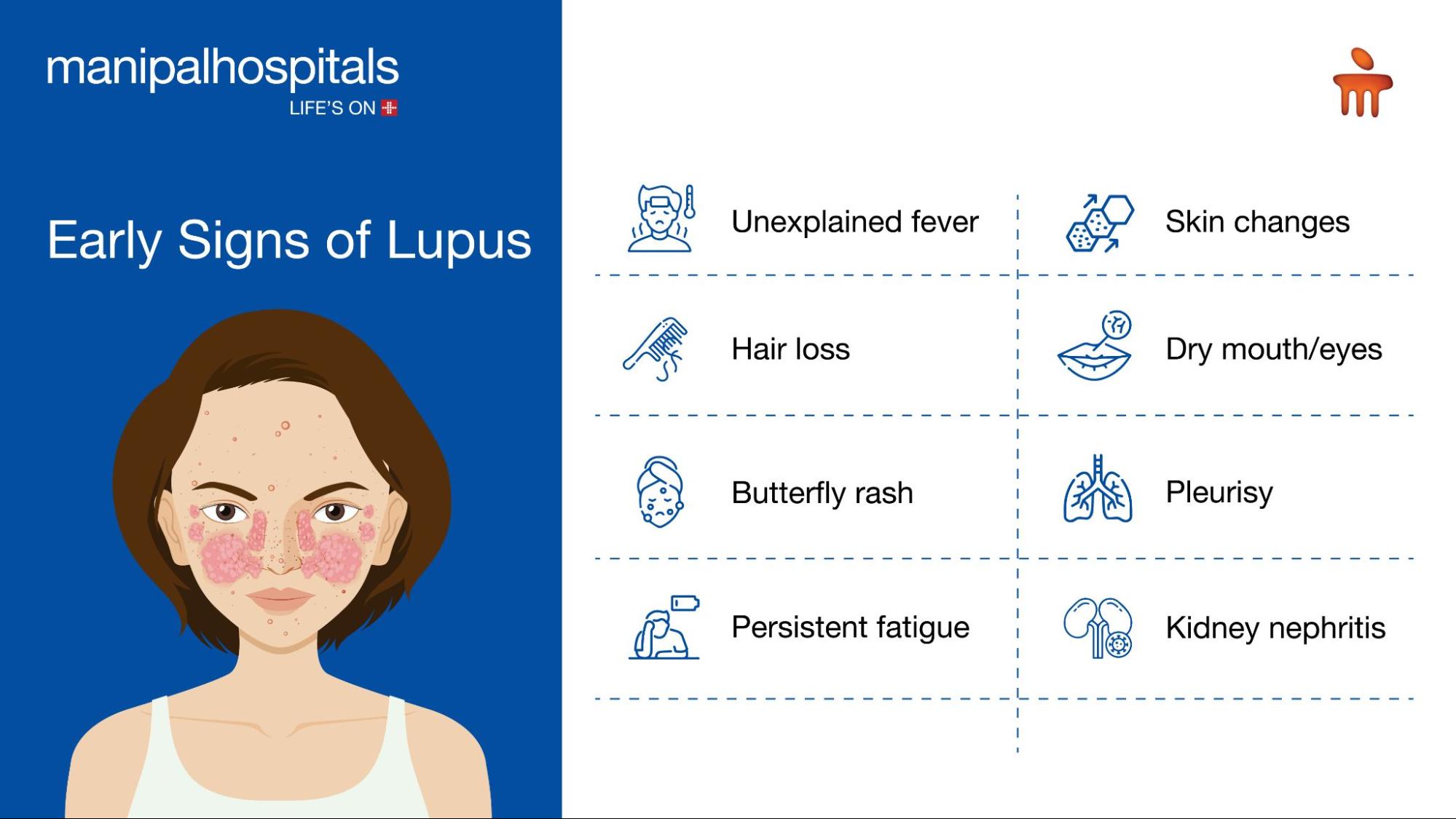
Recognising the early signs and symptoms of lupus can be challenging, as they often overlap with other conditions and differ from person to person. They also flare up in cycles, getting worse, then improving or even disappearing, making it challenging to spot in its early stages. The signs and symptoms of lupus also depend on which body system is affected.
However, understanding the signs and symptoms of lupus can help in early diagnosis. The common lupus symptoms include:
-
Unexplained fever: Recurring or prolonged low to moderate-grade fever without an apparent cause are an early sign of lupus.
-
Hair loss or alopecia: Losing hair with bald spots or thinning hair is an indication.
-
Butterfly-shaped skin rash: The prominent and most visible symptom of lupus, in which a butterfly-shaped rash appears on both cheeks over the bridge of the nose. It could be sudden or appear after exposure to sunlight.
-
Persistent Fatigue: Extreme fatigue that does not improve with rest may be one of the first signs of lupus.
-
Skin changes: Discoloured spots, swelling around one or both eyes, swollen eyelids, thick, scaly patches of skin, mouth sores, scaly rash on the skin (exposed to the sun), and discolouration in the fingers and toes are other early signs of lupus.
-
Lupus nephritis: An inflammation of the kidney with proteinuria
-
Pulmonary issues: Such as pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura, the tissue that protects and cushions the lungs) or effusion
-
Joint Pain or Swelling: If you notice unexplained joint pain, muscle aches, stiffness, or swelling, particularly in the small joints of the hands, wrists, or knees, it could be an early sign of lupus
-
Central nervous system: Severe uncontrollable headache, seizure or psychosis can be a manifestation of CNS involvement in lupus
-
Gastrointestinal issues: These include signs like occasional heartburn, acid reflux etc.
-
Thyroid diseases: People suffering from lupus are more susceptible to developing autoimmune thyroid diseases.
-
Other symptoms: Some people suffering from lupus may also exhibit uncommon symptoms like dry mouth and eyes, anaemia, dizziness, seizures, headache, memory loss, chest pain when taking a deep breath, sores on the scalp, abnormal blood clotting, enlarged lymph nodes, depression, osteoporosis, etc.
What are the Lupus Disease Causes?
The exact lupus disease causes are unknown, but several factors can trigger its onset. These include:
-
Genetics: A family history of lupus or other autoimmune diseases can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
-
Hormones: Reproductive women are more likely to develop lupus, suggesting that hormones, like oestrogen, may play a role in the disease.
-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to sunlight, certain infections, or medications can trigger lupus symptoms in people genetically predisposed to the disease.
-
Immune System Dysfunction: Abnormal functioning of the immune system leads to the production of autoantibodies that attack healthy cells.
What Are the Treatments for Lupus?
There is no particular cure for lupus, but early diagnosis and treatment can minimise organ damage, manage symptoms, prevent flare-ups and improve quality of life. Medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antimalarials, corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, and biologics are recommended to manage lupus. In some cases, a combination of drugs is prescribed for effective treatment.
Conclusion
Lupus is a complex and chronic autoimmune condition that can significantly impact daily life. Recognising the early signs and symptoms of lupus is essential for timely treatment and preventing serious complications. A child can lead a normal life with medications and follow if diagnosed early.
If you or someone you know experiences symptoms such as persistent fatigue, joint pain, a butterfly-shaped rash, unexplained fever, or photosensitivity, it is important to seek medical advice from rheumatology experts at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur. Early diagnosis and treatment can enable individuals with lupus to lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.
FAQ's
Lupus, or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy cells and tissues, leading to inflammation and damage. It can affect multiple organs like the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and brain.
Diagnosing lupus can be difficult, as no single test can diagnose the condition. Signs and symptoms of lupus can also be similar to other conditions. Doctors use a combination of methods to diagnose the disease. These include understanding medical history, performing a physical exam, and undergoing screenings like blood, urine, and imaging tests.
Lupus is difficult to diagnose because its symptoms often overlap with other conditions and can flare up in cycles. Additionally, symptoms vary from person to person and affect different organs.
There is currently no cure for lupus, but with proper management, many people with lupus can lead healthy, active lives.
Lupus can affect daily life by causing fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and other symptoms. However, with effective treatment and lifestyle adjustments, most people with lupus can manage their symptoms and continue with normal activities.
Preventing lupus is unclear, but its flare-ups can be reduced or prevented by avoiding sun exposure, staying active, getting a good night's sleep, and protecting mental health.
Lupus disease can lead to severe complications, such as:
-
Organ failures
-
Chronic pain and fatigue
-
Kidney failure
-
Congenital heart block in babies
-
Infections or other autoimmune diseases
-
Hip destruction
-
Stroke or heart attack
-
Pregnancy complications
Lupus is a chronic disease that can get life-threatening only in rare cases. Generally, all the common forms of lupus are milder, and people can enjoy a good-quality life with the right treatment and medications.
There is no cure for lupus, but treatments aim to manage symptoms and prevent organ damage. Common treatments include:
-
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): For pain and inflammation.
-
Antimalarials: To control skin symptoms and joint pain.
-
Corticosteroids: For reducing inflammation.
-
Immunosuppressive drugs: To control the immune response.
-
Biologics: Target specific components of the immune system.
While medications are key to controlling lupus, some home remedies can complement treatment:
-
Avoid Sun Exposure: Sunlight can trigger flare-ups, so use sunscreen and wear protective clothing.
-
Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids) can help manage symptoms.
-
Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness can reduce stress, which may trigger flare-ups.
During a flare-up, it's important to:
-
Follow your prescribed medication regimen.
-
Rest and take breaks to manage fatigue.
-
Stay hydrated and avoid triggers (e.g., stress, sun exposure).
-
Monitor symptoms and seek medical advice if they worsen.
You can schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, by contacting us or visiting our website.
Visit: https://www.manipalhospitals.com/mukundapur/
Contact no: 03369070001



















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read










