Liver diseases have become a public health priority in India, as they contributed to 18.3% of the 2 million liver-related deaths globally in 2015. Among the various liver diseases, cirrhosis stands at the 11th rank, while liver cancer is the 16th most common cause of death globally1. Alcohol and viral hepatitis are the main causes of liver cirrhosis. Understanding the causes of liver disease and treating and managing them early can improve lifespan. In this blog, we will explore the symptoms to watch for, the top five causes of liver disease, and their impact on your overall health.
Synopsis
What are Liver Diseases?
The liver is one of the most vital organs, without which you cannot live. It is responsible for performing various essential functions, including detoxification of toxins, metabolism, and the production of bile and blood-clotting proteins. When the liver gets compromised due to liver diseases, it can lead to severe health issues as your whole body gets affected. These diseases affect the liver's ability to function properly and can be either acute or chronic. Though the liver cells can regenerate, prolonged damage can lead to severe consequences such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Symptoms of Liver Diseases
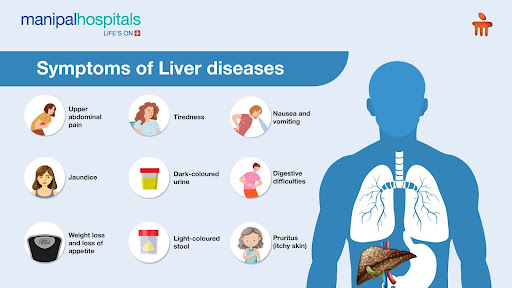
Liver diseases often do not show any symptoms in their early stages. They are usually found during routine blood tests or the diagnosis of other problems, like kidney diseases. Symptoms of liver diseases also depend on the underlying cause and its severity. Its common symptoms include:
-
Tiredness
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Dark-coloured urine
-
Digestive difficulties
-
Weight loss and loss of appetite
-
Light-coloured stool
-
Pruritus (itchy skin)
-
Easy bruising and bleeding
If these symptoms persist, book an appointment with our best Medical Gastro Specialist in Mukundapur.
Causes of Liver Disease
The causes of liver diseases include:
1. Viral Hepatitis Infections
Viral infections, mostly caused by hepatitis viruses (Hepatitis A, B, and C), are significant causes of liver disease. These infections can lead to chronic inflammation, liver damage, and an increased risk of liver cancer. The source of these viruses is bad food, water, or close contact with the blood or semen of an infected person.
2. Alcohol Consumption
Chronic alcohol consumption is a leading cause of liver diseases such as fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and alcoholic hepatitis. Excessive alcohol consumption damages liver cells, leading to inflammation and scarring. Your liver may get damaged beyond repair, so it's important to stop drinking once you see fatty liver symptoms and seek treatment.
3. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease, involves the build-up of excess fat in liver cells, which causes inflammation and scarring (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis). It is associated with obesity, diabetes, high blood lipids, and metabolic syndrome.
4. Autoimmune Diseases
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells or bile ducts, leading to chronic inflammation, damage, and scarring of your liver or bile ducts. Its diseases are autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC).
5. Genetic Disorders
Carrying a liver disease gene from one of the parents can affect the liver's ability to process and store minerals properly, leading to chronic liver damage. Genetic liver disorders are hemochromatosis (iron overload), Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Wilson's disease (copper accumulation), glycogen storage disease, and Gaucher disease.
Effects of Liver Disease on Your Health
The liver plays a crucial role in various body functions. If liver diseases are not treated on time, they can have widespread effects on your health, causing complications such as:
-
Ascites and Oedema: Liver diseases cause a build-up of body sodium that leads to fluid accumulation in the abdomen, called ascites. It is called oedema when it occurs in the extremities, like the legs, feet, or back. These cause discomfort and increase the risk of infection.
-
Metabolic Dysfunctions: The liver is responsible for metabolism, but liver diseases lead to metabolic dysfunction, contributing to conditions like diabetes and malnutrition by interfering with blood sugar regulation, lipid metabolism, and protein synthesis.
-
Detoxification Impairment: The liver serves as the best detox for the body, but in the case of a damaged liver, it cannot effectively detoxify the body. This leads to the accumulation of toxins and potentially causes hepatic encephalopathy, which affects brain function and can lead to coma.
-
Excessive Bleeding: The liver produces proteins responsible for blood clotting. Liver disease can result in reduced production of these proteins, leading to excessive bleeding and easy bruising. Also, cirrhosis can block the vein passing through the liver, leading to its rupture and bleeding in the gastrointestinal system.
-
Jaundice and Pruritus: Impaired production of bile and its secretion causes jaundice and severe itching, called pruritus, significantly impacting your quality of life.
-
Liver Failure: If left untreated, the liver disease progresses to liver failure as cells get destroyed much faster than the liver can replace them. It is a life-threatening condition.
Conclusion
Liver diseases have become an alarming situation, so understanding their main causes and recognising early symptoms are crucial for preventing and managing them effectively. If you suspect you have liver disease or are at risk of liver failure, seek immediate medical advice at our Gastroenterology Hospital at Mukundapur, providing the proper diagnosis and treatment of liver diseases. Early intervention and regular monitoring can significantly reduce the risk of liver disease and ensure better patient outcomes. Check out our blog page for the latest updates in the medical world.
FAQ's
Various factors increase the risk of liver diseases, including:
-
Type-2 diabetes
-
Excessive consumption of alcohol
-
Obesity
-
Using intravenous drugs
-
Exposure to toxic chemicals
-
Family history of liver disease
-
Tattoos or body piercings
-
Unsafe sex
-
Contact with other people's blood or bodily fluids
The doctor will do a physical examination, look for any visible signs, check the medical history, and order some diagnostic tests for confirmation and determination of the extent of the disease.
The diagnostic tests include the following:
-
Blood tests: liver function test
-
Imaging tests: abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, MRI
-
Elastography
-
Endoscopy
-
Nuclear medicine imaging
-
Liver biopsy
The treatment of liver diseases depends on their cause and type, but early recognition helps in curing liver diseases before permanent damage occurs. Its various treatment options are:
-
Lifestyle modifications and dietary changes
-
Medications such as anti-virals, steroids, antibiotics, blood pressure moderators, vitamins, and supplements
-
Surgery
-
Liver Transplant
For personalised treatment recommendations, get in touch with our liver specialists.
Lifestyle changes can help prevent and manage certain liver diseases. Follow these tips:
-
Eat a well-balanced diet
-
Stay physically active
-
Avoid smoking
-
Maintain a moderate weight
-
Limit consumption of alcohol
-
Annual body checkups
-
Doing a safe sex
-
Get vaccinated against Hepatitis A and B
-
Take medicines only when needed
-
Keep your food safe
-
Stay away from harmful chemicals
To schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, contact our Gastrointestinal Department or visit our website.



















 4 Min Read
4 Min Read





.png)








