Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the predominant causes of liver disorders in children, resulting from unhealthy lifestyle choices. The fat that accumulates in the liver, when left untreated, can cause severe complications into adulthood. The prevalence of NAFLD among Indian children is rising and currently stands at 35.4%. Therefore, patients must be aware of NAFLD and the factors leading to it. This blog post contains all the necessary information to safeguard your child’s liver.
Synopsis
About Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Now known as Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease or MASLD)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common kind of chronic liver disease in children and adolescents. When too much fat accumulates in the liver cells, NAFLD develops.
Normally, the liver absorbs nutrients straight from the stomach and converts fat, carbohydrates, and protein into other energy sources. Excess fat in the liver may arise from an imbalance in this mechanism.
NAFLD is a collective name for conditions that manifest in varying stages:
-
Simple steatosis: the accumulation of fat in the liver.
-
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): inflammation (liver swelling) brought on by fat accumulation (formerly known as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, or MASH).
-
NASH combined with fibrosis: the formation of liver scarring.
-
Cirrhosis: liver stiffening and lumps (nodules), typically as a result of chronic injury; this may lead to liver failure.
Risks of Developing NAFLD in Childhood
Children may be more susceptible to NAFLD if they
-
Are obese
-
Have insulin resistance, which causes blood sugar to rise.
-
Have type 2 diabetes
-
Consume unhealthy foods (foods with excessive sugar or fat content) and exercise infrequently or never.
-
Have extremely high blood levels of fat or cholesterol (dyslipidemia).
-
Have uneven breathing patterns when they sleep, or sleep apnea.
Though the extent to which genetics contributes to the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is unknown, there may be a hereditary (genetic) risk.
Symptoms of NAFLD
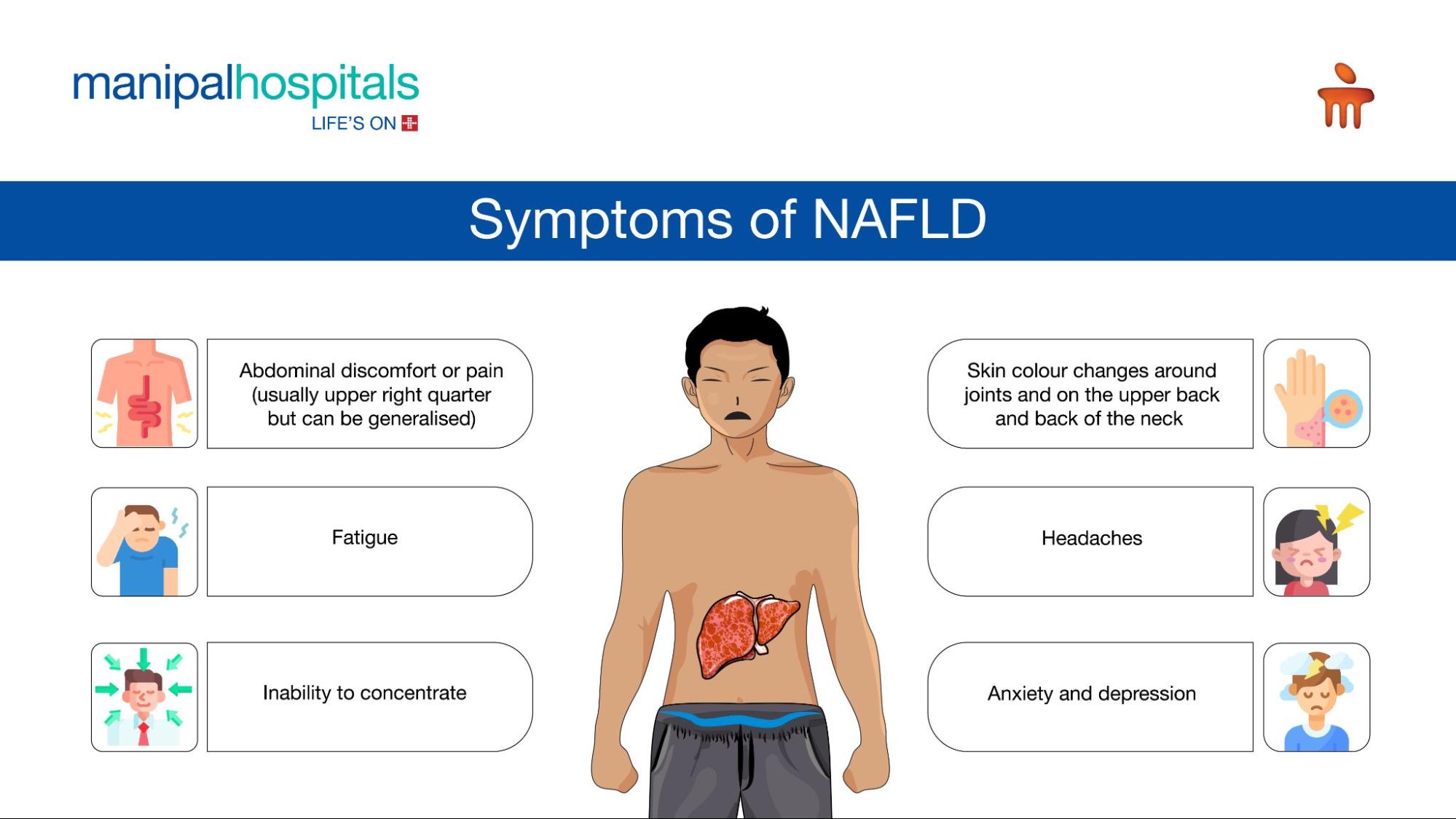
Early on, NAFLD does not exhibit any symptoms. It is more typical for symptoms to appear after the liver has sustained substantial damage. The following are a few signs of NAFLD:
-
Abdominal discomfort or pain (usually upper right quarter but can be generalised).
-
Fatigue
-
Headaches
-
Inability to concentrate
-
Anxiety and depression
-
Skin colour changes around joints and on the upper back and back of the neck
Consult our paediatrician in Kolkata if you are experiencing the above nonalcoholic fatty liver disease symptoms.
Diagnosis of NAFLD
A medical professional may first perform a physical examination to identify any symptoms or indicators of liver disease. The next step is to use blood tests to assess liver function and monitor liver enzyme levels, which can show inflammation and damage to the liver.
Clinicians can identify fat accumulation and evaluate liver function with the help of imaging procedures like:
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
-
Computed tomography (CT) scans
-
Ultrasound
These provide precise images of the liver. A liver biopsy may be suggested in certain circumstances to verify the diagnosis and gauge the extent of liver damage.
Consult our paediatric hospital in Mukundapur Kolkata if you need NAFLD diagnosis and NAFLD treatment.
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment
Children with NAFLD are usually treated with:
-
Lifestyle changes: Promoting a well-balanced diet with lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats.
-
Weight management: Children's liver fat buildup can be considerably decreased by helping them reach and maintain a healthy weight through dietary adjustments and increased physical exercise.
-
Medical Monitoring: To monitor fatty liver disease treatment, evaluate progress, and modify treatment as necessary, regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial.
-
Education and support: By educating children and their families about non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), stressing the need to adopt healthy lifestyle practices, and following treatment, we can enable them to take charge of their health and achieve better results.
-
Handling Comorbidities: Improving general health and avoiding NAFLD consequences can be achieved by treating and controlling underlying problems such as obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome with lifestyle modifications and if needed, medication.
Insights for Parents on NAFLD in Children
Children's non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is becoming more prevalent as a result of unhealthy lifestyles, is something that parents should be aware of. Because symptoms can be mild, frequent testing is crucial for early detection. Regular medical check-ups are frequently the means of making a diagnosis, underscoring the importance of preventive healthcare. The mainstay of treatment is changing one's lifestyle to include regular exercise and a balanced diet. Therefore, parents must be alert for symptoms such as exhaustion and stomach pain, which should prompt medical attention if NAFLD is suspected. To promote healthy habits and encourage open communication with healthcare practitioners, family involvement is essential. Parents can have a major impact on their children's liver health and general well-being by being proactive and knowledgeable, which may also stop NAFLD from progressing to more serious diseases.
Conclusion
NAFLD liver among children is a preventable condition with the right choices and implementing preventive measures. Therefore, educating parents is a crucial aspect of reducing the disease burden. Manipal Hospitals prioritises early detection through modern diagnostic procedures and offers customised treatment plans emphasising lifestyle adjustments. The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and a staff of trained specialists to provide comprehensive care for your child.
FAQ's
Parents have a direct role in fostering a home atmosphere that encourages a healthy diet and regular exercise. Promoting open communication between patients and healthcare professionals makes it possible to identify any changes in a child's condition early on, allowing for timely intervention and necessary treatment modifications. By working together, parents can best support their child's general health and liver function.
Preventing the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) into more severe liver disease and its related consequences requires early detection and intervention. It's imperative to get regular medical checkups and screenings.
In children, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) can be effectively managed and may even be resolved or improved with time with early detection and proper lifestyle modifications. More extensive therapies, however, might be required in some circumstances, especially if the condition has advanced to the point of NASH, or liver fibrosis.
For individualised advice and assistance, parents can speak with paediatricians, paediatric gastroenterologists, or other healthcare professionals. Good medical websites, support groups, and liver health-focused organisations can also offer helpful information and tools.
To schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, contact our hospital or visit our website.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read