-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Cancer Care/Oncology
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- Gastrointestinal Science
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Organ Transplant
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Rheumatology
- Spine Care
- Urology
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Children’s Airway & Swallowing Centre
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Laboratory Medicine
- Lactation
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Cancer Care
- Paediatric Cardiology
- Paediatric Endocrinology
- Paediatric General Surgery
- Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Paediatric Neurology
- Paediatric Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplant
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Psychology
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Renal Sciences
- Reproductive Medicine
- Robotic Assisted Surgery
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
- Doctors
- Mukundapur
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
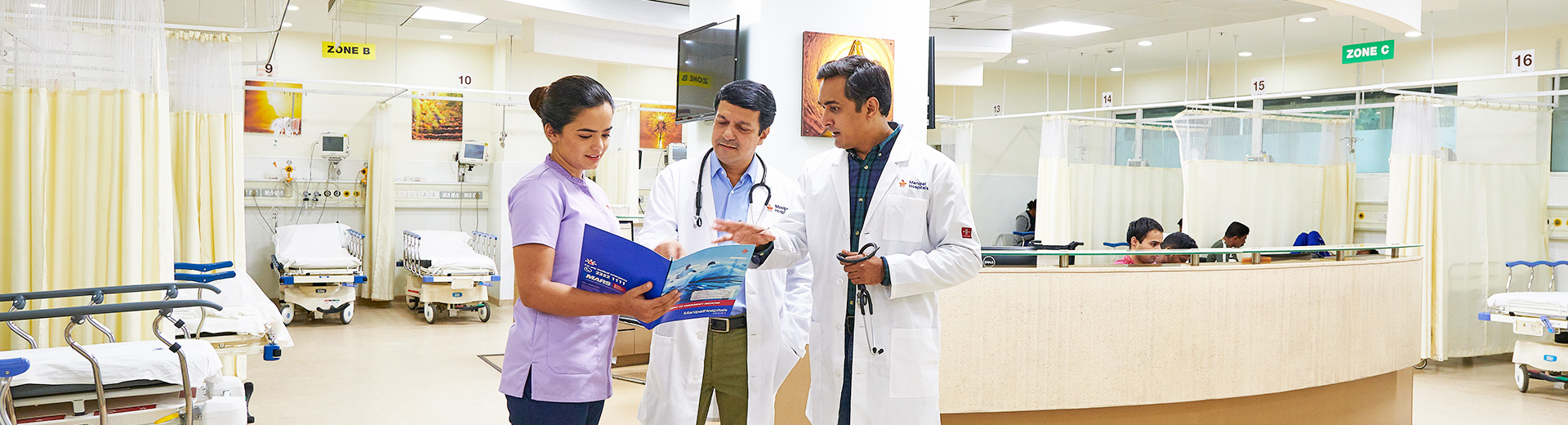

Colposcopy Clinic
Best Colposcopy Examination Hospitals in Mukundapur
A Colposcopy examines any abnormal parts of your cervix and vagina. A specialist (Colposcopist) will employ a magnifying tool called a colposcope, which appears like a pair of binoculars on a stand. A Colposcopy is normally performed in a hospital or clinic. The Colposcopy takes about 15 to 20 minutes, and one can go home afterwards. However, you may have to stay at the hospital for several hours before leaving to check for any complications that may arise after the procedure. When you arrive at the hospital or clinic, a nurse will explain what will happen during the Colposcopy. The doctor will ask you questions about your medical history, current health, allergies, and recent travel history. A Colposcopy test is typically recommended when your pap test or cervix self-screening sample reveals a high-risk type of human papillomavirus (HPV): HPV 16 and/or 18.
The Colposcopy Clinic at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, provides diagnostic services, including Colposcopy and biopsy procedures, to detect precancerous changes, HPV infections, and other abnormalities. The goal is early detection and management of potential cervical and other gynaecological cancers to ensure effective treatment and better patient outcomes.
FAQ's
Colposcopy is used by the doctor to examine the cervix, or opening to the uterus, as well as the vagina. It employs a colposcope, which consists of a magnifying lens and a light. It magnifies the image numerous times. The healthcare provider can see the tissues on the cervix and vaginal walls more clearly. In some situations, your provider will collect a small sample of tissue for testing in the lab. This is known as a Cervical Biopsy.
Two areas can be examined during a Colposcopy:
-
Cervix: The lower, narrow section of the uterus is positioned between the bladder and the rectum, producing a canal that exits into the vagina and leads to the outside of the body.
-
Vagina: This is the channel via which fluid exits the body during menstruation. The vagina connects the cervix to the vulva (outer genitalia).
You may require Colposcopy if:
-
You have had two or more positive tests in succession for human papillomavirus (HPV).
-
If a cervical screening test (smear test) reveals abnormal cells in your cervix, the doctor may consider your cervix to be unhealthy.
-
If multiple screening tests yield negative results, your doctor may refer you for a Colposcopy if you exhibit symptoms of cervical cancer.
Don't be concerned if you're informed you'll require a Colposcopy, as it's necessary to rule out any suspicion. You must attend your Colposcopy appointment, even if you are pregnant.
A Colposcopy may be performed at your doctor's office or while you are in the hospital. Procedures may differ depending on your condition and the method used by your healthcare provider. A Colposcopy typically involves the following steps:
-
You will need to undress entirely, or from the waist down, and change into a hospital gown.
-
You will need to empty your bladder before the procedure
-
You will lie on an exam table with your feet and legs supported, much as you would do for a pelvic examination.
-
Your healthcare professional will place a speculum into your vagina to spread the vaginal walls apart, exposing the cervix.
-
Then will insert the colposcope, which resembles a microscope with a light on the end, into the opening of your vagina.
-
The colposcope does not enter the vagina. Your healthcare professional will use the colposcope to look for any issues on the cervix or in the vagina.
-
Your provider may clean and immerse your cervix with a vinegar solution, often known as an acetic acid solution.
-
This solution helps to turn the aberrant tissues white and more noticeable. You may get slight burning sensations. The Schiller test involves using an iodine solution to cover the cervix.
-
Your healthcare professional may also perform a biopsy, which involves extracting a small tissue sample. When this is completed, the area is numbed, although you may experience a minor pinch or cramp as the tissue is removed.
-
Your physician may collect a sample of cells from the interior of the cervical canal. This may also produce cramps.
-
To address bleeding from the biopsy site, your clinician may administer a paste-like topical medication or apply a pressure dressing. The tissue will then be sent to a laboratory for testing.
Colposcopy is a very safe procedure, but your nurse will advise you on whom to contact if you experience any concerns after your test. Your doctors verify that the benefits of undergoing a Colposcopy outweigh its hazards. These include
-
Following a biopsy, you may experience minor bleeding for up to 5 days, which is normal. If the bleeding is more than usual or if it continues after a week, consult the doctor or the Colposcopy clinic for guidance.
-
Infection: There is a tiny chance of infection. If you become infected, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
You should avoid having intercourse and using tampons until any bleeding has stopped, which should be around 5 days after a biopsy. This helps the cervix to heal while lowering the chance of infection. If you’re pregnant, you can have a Colposcopy while pregnant. It is completely safe for both you and the baby and will have no effect on the birth. It will also not impair your capacity to become pregnant in the future.
You can go home as soon as the Colposcopy is completed. When people get up after surgery, they may feel dizzy or faint. If you're feeling this way, the nurse will ask you to lie down. They will monitor you until you have recovered and are ready to return home. If you have a biopsy, you may experience discomfort, similar to period pain, for the next few hours. You can take regular pain relievers to alleviate the pain.
Most women who visit the Colposcopy clinic must have a cervical screening test every 12 months until two consecutive tests are negative. Then, most women will be able to have a test every five years.
A Colposcopy is rather painless. When you insert the speculum, you may feel pressure. When they wash your cervix with a vinegar-like solution, it may sting or burn slightly. If you get a biopsy, you may feel some discomfort.
Following a Colposcopy, it is critical to listen to your body and relax as needed. What seems right for someone else may not be suitable for you. If you've had a biopsy, you may feel fine to resume your normal workout routine right away. If you've undergone treatment, your recovery time may be prolonged.
Home Mukundapur Specialities Cancer-care Colposcopy-clinic

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services










