-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Cancer Care/Oncology
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- Gastrointestinal Science
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Organ Transplant
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Rheumatology
- Spine Care
- Urology
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Children’s Airway & Swallowing Centre
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Laboratory Medicine
- Lactation
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Cancer Care
- Paediatric Cardiology
- Paediatric Endocrinology
- Paediatric General Surgery
- Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Paediatric Neurology
- Paediatric Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplant
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Psychology
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Renal Sciences
- Reproductive Medicine
- Robotic Assisted Surgery
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
- Doctors
- Mukundapur
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
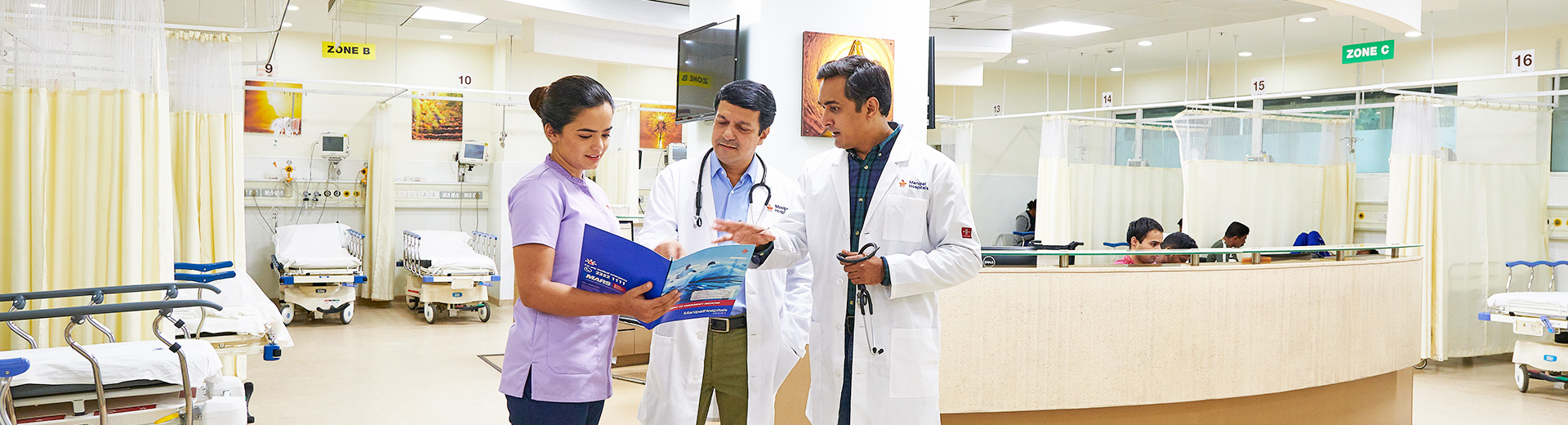

Chronic Diseases
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Treatment In Mukundapur
The diseases that affect the gastrointestinal (GI) tract are called gastrointestinal diseases, GI diseases, or digestive disorders. The GI tract comprises the passage between the mouth and the anus. Though GI diseases are common if they last for months or years, these GI diseases become chronic and affect your quality of life.
The most common chronic gastrointestinal diseases are Crohn’s disease, irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease. These diseases lead to persistent symptoms, significantly affecting your day-to-day activities. Treating and managing these diseases is crucial to preventing long-term and serious complications. These can be handled by making certain lifestyle modifications, medications, and dietary changes to alleviate the symptoms. GI surgery may be needed in severe cases to improve function. The type of GI surgical intervention will depend on the type of disease, its cause, and your condition.
Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, has a team of skilled gastrointestinal surgeons experienced in performing GI surgeries with precision, thereby preventing disease progression, reducing symptoms, and enhancing patient’s overall well-being. With a lot of advancements in surgical techniques, we employ the latest surgical methods to provide comprehensive care and improve patient outcomes for patients with chronic GI diseases, helping them lead more manageable and fulfilling lives.
FAQ's
Chronic gastrointestinal diseases are the ones that last for months, years, or life-long. The most common diseases are:
-
Crohn’s disease: This disease affects the lining of the digestive tract and is a chronic type of inflammatory bowel disease. Chronic inflammation can spread from the stomach to the anus and can become life-threatening. This can cause symptoms like abdominal pain, severe diarrhoea, fatigue, weight loss, and anaemia.
-
Ulcerative Colitis: This is another type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes long-lasting inflammation and ulcers in the superficial lining of the colon and rectum. The condition can be mild to severe, but it increases your risk of developing colon cancer. Symptoms include bloody diarrhoea, rectal bleeding, abdominal cramps, or pain.
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A chronic condition affecting the large intestine. It causes symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating and gas, physical weakness, and constipation.
-
Coeliac Disease: This is a chronic digestive and immune disorder caused by eating foods containing gluten, which damages the small intestine. This causes long-lasting digestive problems and symptoms like diarrhoea, gas, fatigue, bloating, and osteoporosis.
There are two types of gastrointestinal diseases:
-
Functional Digestive Diseases: In these diseases, the GI tract looks normal but does not function properly. These are characterised by chronic GI symptoms and are most common, affecting the GI tract, including the colon and rectum. Diseases include irritable bowel syndrome, functional dyspepsia, and acid reflux.
-
Structural Digestive Diseases: In these diseases, the bowel looks abnormal and even does not work properly. Surgery is needed in some cases to remove structural abnormalities. Structural issues may arise anywhere in the GI tract. Its diseases include haemorrhoids, colon polyps, colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticular disease, stenosis, and strictures
The exact cause of gastrointestinal diseases is not fully understood. But several factors can contribute to these diseases, such as:
-
Genetics (family history of GI disease)
-
Environmental factors such as smoking, stress, depression, and medication
-
Immune system: An abnormal immune response can lead to conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. An autoimmune response to gluten leads to coeliac disease
-
Gut microbiome: Imbalances in gut bacteria can cause diseases like IBS and IBD
-
Less water intake and a low-fibre diet
-
Dairy foods
-
Ageing
For diagnosing chronic GI diseases, the doctor will evaluate your medical history, conduct a physical examination, and make you undergo various diagnostic tests. These include:
-
Blood tests like faecal occult blood tests
-
Stool culture
-
Imaging tests like the colorectal transit study, barium beefsteak meal, CT scan, MRI, ultrasound test, and radioisotope gastric-emptying scan
-
Endoscopic procedures like Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography, Colonoscopy, Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (Upper Endoscopy)
-
Elimination diet and food sensitivity test
Chronic GI diseases require surgical treatment to improve quality of life and prevent further complications. The type of surgical treatment will depend on the specific GI condition, its severity, and your medical condition. The surgical methods can be done through minimally invasive or open surgery techniques. The commonly employed GI procedures are:
-
Appendectomy
-
Nephrectomy
-
Colon and Rectal Surgery
-
Splenectomy
-
Hiatal Hernia Repair
-
Proctocolectomy with Ileostomy
-
Proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA)
-
Whipple Procedure (Pancreaticoduodenectomy)
-
Roux-en-Y
-
Nissen Fundoplication
-
The recovery after any GI surgery will depend on the type and extent of the surgery performed.
-
You may need to stay in the hospital for a few days to a few weeks, depending on the complexity of the procedure.
-
You may be given pain medications to relieve pain after the surgery.
-
Take care of your diet; often, a liquid diet is recommended when starting.
-
Also, make long-term dietary changes for better healing.
-
Resting is very important to prevent complications.
-
Gradually return to your normal activities, as advised.
-
Don’t forget to come for regular follow-ups, as it helps in monitoring your health, identifying any complications, and making any adjustments to medications or treatment plans.
Though it's beneficial for patients suffering from chronic GI diseases, it also carries some risks, such as:
-
Infection
-
Bleeding
-
Formation of scar tissue
-
Anaesthesia issues
-
Nutritional deficiencies
-
Recurrence
Our GI surgeons use their expertise and advanced techniques to improve treatment outcomes and reduce complications.
Chronic GI diseases can be treated and managed without surgery in certain cases. The treatment approach includes:
-
Medications - Anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressants, antibiotics, and biologics to alleviate symptoms
-
Dietary modifications - Tailored diet plans to avoid triggers
-
Lifestyle changes - Regular exercise, reducing stress, and quitting smoking
-
Probiotics - Supplementing with gut bacteria
-
Regular health check-ups
Home Mukundapur Specialities Gi-surgery Chronic-diseases

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services










