-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Cancer Care/Oncology
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- Gastrointestinal Science
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Organ Transplant
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Rheumatology
- Spine Care
- Urology
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Children’s Airway & Swallowing Centre
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Laboratory Medicine
- Lactation
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Cancer Care
- Paediatric Cardiology
- Paediatric Endocrinology
- Paediatric General Surgery
- Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Paediatric Neurology
- Paediatric Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplant
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Psychology
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Renal Sciences
- Reproductive Medicine
- Robotic Assisted Surgery
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
- Doctors
- Mukundapur
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us
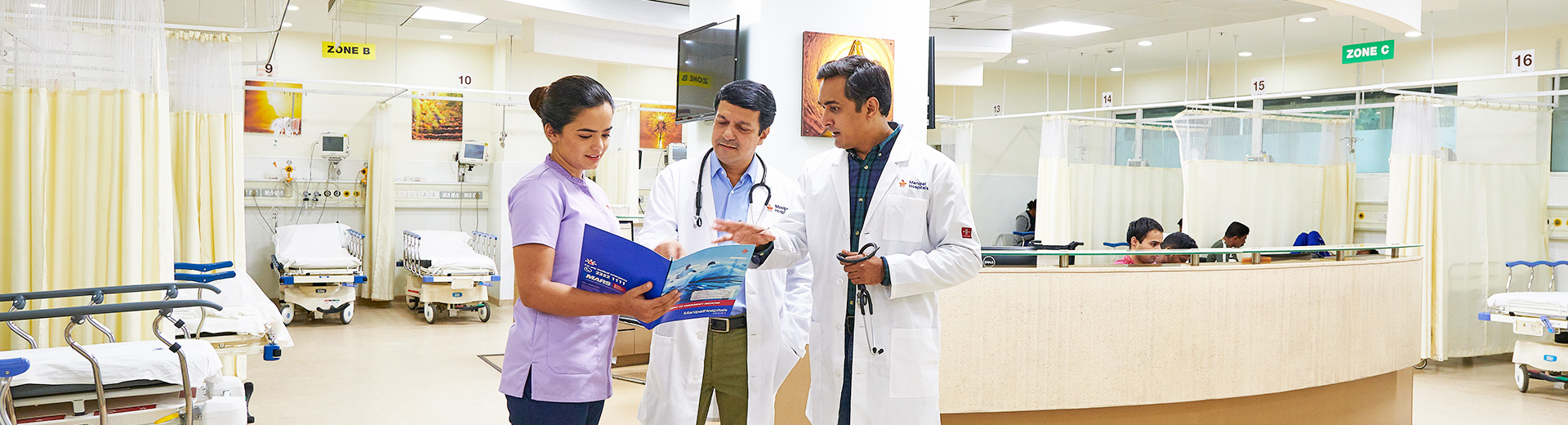

Intramuscular Injections
intramuscular injection
The process of injecting medication into the deep tissue of particular muscles is known as intramuscular injection (IM). Because the large muscles have high vascularity, the injected medication bypasses the first-pass metabolism and swiftly enters the systemic circulation and its targeted site of action. In children, IM injection sites such as the vastus lateralis (thigh) and deltoid (upper arm) can absorb larger volumes of solution because of their rich blood supply. This makes IM injections suitable for administering various drugs, including vaccines, analgesics, antibiotics, and sedatives.
To prevent complications in paediatric patients, intramuscular injections must be administered carefully to the right site and by using the proper technique. Muscle atrophy, bone damage, cellulitis, sterile abscesses, discomfort, and nerve damage are among the complications associated with IM. The risk of injecting the drug straight into the patient's bloodstream is higher when using IMs. Additionally, the pace and degree of drug absorption will be impacted by any variables that reduce blood flow to the nearby tissue.
To ensure the medication reaches the deep muscle tissue in pediatric patients, the needle length and gauge must be selected appropriately, considering the child's age, size, and muscle mass. The needle should be inserted at a 90-degree angle, which differs from the angles used for subcutaneous and intradermal injections. Visit Manipal Hospitals, if you are looking for intramuscular injections in Mukundapur, Kolkata.
FAQ's
The benefits of intramuscular injections are:
-
The medication works quickly because it gets absorbed into the bloodstream faster than other methods.
-
IM injections provide faster results compared to tablets or under-the-skin injections.
-
The medication doesn’t have to go through the stomach or liver first, so it works more efficiently.
-
IM injections avoid problems like acidity or digestion that can affect how medicines work when taken orally.
-
Extremely useful in emergency situations, including acute psychosis and status epilepticus.
-
Some IM injections are designed to release the medicine slowly, providing lasting relief over time.
-
IM injections can handle bigger doses of medicine compared to under-the-skin injections.
The drawbacks of intramuscular (IM) injections are:
-
Intramuscular (IM) injections must be administered by trained healthcare professionals.
-
The effectiveness of the medicine depends on the muscle’s size and blood flow.
-
Once injected, the start and duration of the medicine’s effect cannot be adjusted.
-
In emergencies like severe allergic reactions, other methods (e.g., IV) may be necessary.
-
Administering injections to children or restless patients can be challenging.
-
Incorrect placement may delay the medicine’s effect.
-
Oily or thick medications cannot be administered through IM injections.
-
The process can cause anxiety, especially in children.
-
Self-administration of IM injections is difficult for most patients.
-
Medications may take longer to work if absorption is uneven.
-
Rarely, medicines may stay in the muscle longer than expected, causing delayed effects.
-
Young children or anxious patients may require gentle restraint during the procedure.
Because children have smaller muscle mass than adults, the site cannot absorb higher quantities of medication adequately. So, in infants and small children, no more than 1 ml of medication should be given in a single intramuscular injection. For older children with more developed muscles, up to 2 ml can be administered in a single IM injection. If a larger dose is required, it may need to be divided and injected into different sites to prevent discomfort and ensure proper absorption. The injection volume should always be adjusted based on the child’s age, size, and muscle development.
Vastus lateralis (thigh) and deltoid (upper arm) are frequently utilised for intramuscular injections because they are thought to be safe. The deltoid site is often preferred in clinical settings as it is convenient for both patients and healthcare providers.
The contraindications for intramuscular (IM) injections include:
-
Restrictions at the site of administration, such as dermatitis, cellulitis, or active infection.
-
A documented medication allergy or hypersensitivity.
-
Conditions where muscle enzyme release complicates therapy, such as acute myocardial infarction, thrombocytopenia, and coagulation disorders.
-
Hypovolemic shock, as weakened vascularity in muscles may hinder drug absorption.
-
Myopathies, where muscle atrophy increases the risk of neurovascular complications and delays medication absorption.
A topical numbing lotion applied beforehand or distraction tactics can help reduce the pain. Children may still feel some discomfort during the injection. The amount of pain will depend on the quantity of injection because if more solution is injected into the muscle, more pressure will be applied to the pain receptors, and more damage is done to the muscular bundles, which increases the perception of pain. For paediatric patients, it's particularly crucial to employ the right needle size and technique.
The trick is to communicate. Speak with the professional and clear all your queries. Also, reassure your child that everything is ok. Both you and your child can benefit from deep breathing exercises or relaxation techniques. Distraction techniques can also be used to soothe the child.
Unless your doctor or nurse instructs you otherwise, it is advised that you make your child rest and avoid strenuous activities for the remainder of the day following most injections. Showers are ok, but for a few days, make them stay away from hot tubs, whirlpools, soaking baths, and swimming pools.
Any form of massage should be avoided after receiving intramuscular injections since it may cause the drug to reappear via the subcutaneous tissue.
Home Mukundapur Specialities Paediatric-and-child-care Intramuscular-injections

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services










