-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Cancer Care/Oncology
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- Gastrointestinal Science
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Organ Transplant
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Rheumatology
- Spine Care
- Urology
Other Specialities
- Allergy and Immunology
- Andrology
- Anesthesiology
- Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Children’s Airway & Swallowing Centre
- Clinical Psychology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- Electrophysiology
- Fetal Medicine
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hemato Oncology
- Hematology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Kidney Transplant
- Laboratory Medicine
- Lactation
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Microbiology
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery
- Paediatric Cancer Care
- Paediatric Cardiology
- Paediatric Endocrinology
- Paediatric General Surgery
- Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Paediatric Neurology
- Paediatric Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Parkinson Disease and Movement Disorder
- Pathology
- Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplant
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic And Cosmetic Surgery
- Podiatric Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Psychology
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Renal Sciences
- Reproductive Medicine
- Robotic Assisted Surgery
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Transfusion Medicine
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
- Doctors
- Mukundapur
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- Mars - Ambulance
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Careers
- Contact Us

Pediatric Trauma
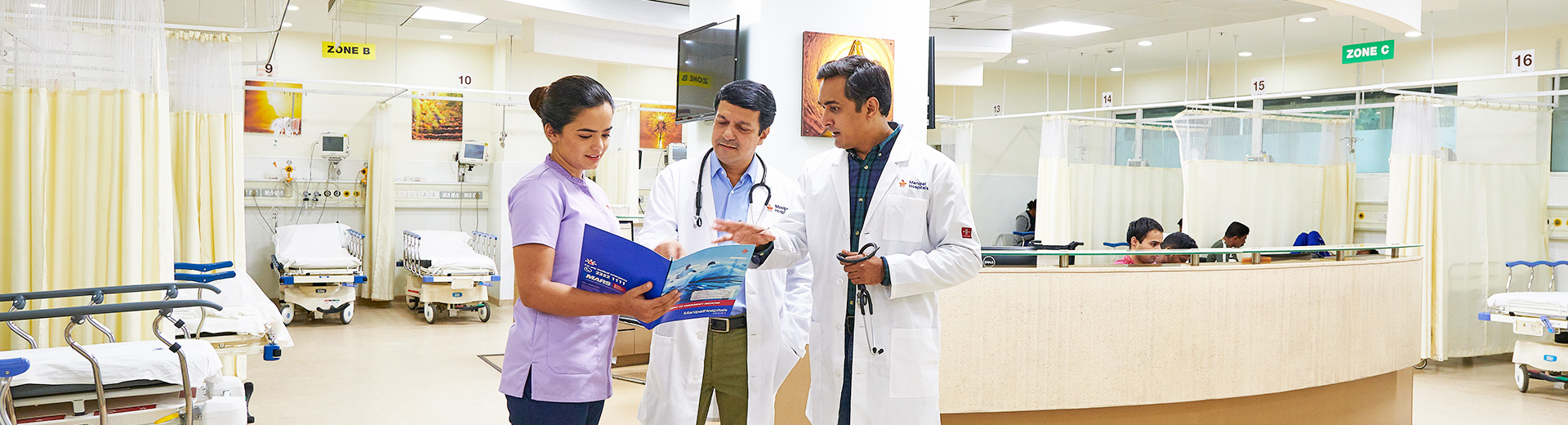
Paediatric Trauma Treatment in Mukundapur, Kolkata
Paediatric traumas are injuries that affect major organs, such as the brain, lungs, heart, kidneys, and liver, due to road accidents, falls, burns, or other forms of impact. The injuries can vary from minor cuts to bruises, and failure to provide timely intervention can lead to severe and life-threatening conditions. Paediatric trauma is a leading cause of child mortality and morbidity, with India having a significant share of paediatric deaths and DALY (known as Disability-Adjusted Life Year, a measurement used to assess the quality of life and length of children affected with disabilities), especially in children aged 0-14 years old.
The Paediatric and Child Care Department at Manipal Hospitals, Mukundapur, Kolkata, ensures providing comprehensive care for paediatric patients diagnosed with trauma-related injuries by leveraging state-of-the-art technologies and offering swift and tailored emergency services. Our highly experienced specialists in Paediatric Trauma Treatment in Mukundapur, Kolkata, are trained in treating challenging trauma cases, enabling them to provide efficient care and management, along with nurses and support staff dedicated to round-the-clock assistance throughout their treatment.
FAQ's
Any injury that the child gets in the head or brain during their birth, childhood, or early teenage years is called Paediatric Trauma. Traumas mostly happen due to sudden falls or accidents. Traumas are one of the leading life-threatening conditions in children, as they directly affect the brain if the injury is severe.
Some early signs and symptoms of trauma injury include:
-
Physical Indications
-
Headache(s)
-
Light sensitivity, sound sensitivity
-
Vomiting or feeling nauseous
-
Experiencing fatigue or drowsiness
-
Lightheadedness
-
Breathlessness
-
Double or hazy eyesight
-
Signs of Cognitive (Brain) Functioning
-
Feeling disoriented or unclear
-
Sluggish processing or sluggish thinking
-
Memory problems
-
Unable to focus
The types of airway defects that a child may have include:
-
Blockage of the upper airways at the voice box
-
Obstruction of the lower airways that arises at the intersection of the larynx and small passageways
-
Partial blockage of the airway that permits some air to flow
-
Total blockage of the airways prevents the passage of any air; respiration is impacted
-
The foreign item immediately causes acute airway blockage
-
Chronic airway blockages that may not appear for a long time or that will not go away quickly
Falls, car crashes, poisonings, burns from hot liquids or steam, and poisonings are the most common types of Paediatric Trauma injuries.
The doctor treating your kid will inquire about the nature of the injury as well as any following symptoms. Your kid could have a physical and neurological assessment, depending on the extent of the damage. Their memory, reasoning, attitude, conduct, eyesight, and focus will all be tested by the physician. Your child's reflexes, sensation, muscle strength, balance, and coordination will also be tested. Rarely, a CT or MRI scan may be required to assist in determining the severity.
Assisting with immediate medical requirements, creating a safe environment, and offering emotional support are the first objectives of care for children who have suffered trauma injuries. The treatment approach includes providing symptomatic relief and performing necessary procedures if required.
-
The treatment approaches for Paediatric Trauma include:
-
Resting
-
Icing the site of injury
-
Antibiotic cream applied topically
-
Application of bandages and secondary dressings to prevent bleeding
-
Stitches
-
Keeping the child in the hospital under observation
-
Prompt surgical intervention when required.
For children that have minor injuries, the doctors might just ask that they take adequate rest with the least physical activities until they heal completely.
Teaching your children about all forms of safety measures is incredibly essential. Ensuring your child is safely fastened up in an age-appropriate seatbelt is crucial for every car journey. If they are involved in activities like cycling or skating, ensure that they have all the safety equipment with them. Very specific care should be taken for toddlers, as they are at the highest risk of getting traumatised. All harmful things, such as electronics, metals, lighters, and sports equipment, should be kept away from toddlers. They should be constantly supervised at home and any spot that is risky for your child should be secured by taking appropriate measures.
If the trauma injury was caused by a serious event, there are several things that the child may experience even after recovering, which include:
-
Recalling the experience through flashbacks, nightmares, intrusive memories, etc.
-
The constant fear that the injury/accident might happen again
-
Constant feelings of unhappiness
-
Not wanting to go outside and preferring to stay inside more often
-
Not getting involved in their regular hobbies
-
Not memorising some particular events from the trauma
-
Sleeplessness
-
Irritability
-
Unconsciousness
-
Overprotectiveness for self
-
Difficulty in focusing
If you feel that there has been a major negative impact of the trauma on your child, there are several things that you can do to help them recover, such as:
-
Reassuring your children that it was just an accident and that it can happen to anyone. Also, it is preventable if you take proper safety measures.
-
Assisting them in all possible activities until they gain their confidence back.
-
Provide them with safety equipment and also teach them all the safety measures to be taken to avoid any such incidents in the future.
-
Accompanying them in their choice of activity also helps children recover, as they understand it's harmless.
-
Arranging small outings with their friends to encourage them to socialise and involve themselves in outdoor activities.
A concussion is a type of brain injury that alters brain function and can cause symptoms including headaches, lightheadedness, and disorientation. With relaxation, a gradual return to school, and regular activities, symptoms often go away in a few days to a month. The symptoms might occasionally linger longer. Concussions are common for children who are involved in sports such as football and hockey. It can happen due to any severe injury that the child gets in the head.
Home Mukundapur Specialities Paediatric-general-surgery Pediatric-trauma

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services










