-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
- Access Lab Reports
-
-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
Other Specialities
- Anesthesiology
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Gastrointestinal Science
- General Surgery
- GI Surgery
- Gynaec Oncology
- Hematology
- ICU and Critical Care
- Internal Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Pain Medicine
- Physiotherapy
- Plastic, Reconstructive And Cosmetic Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Radiology
- Rheumatology
- Surgical Oncology
- Doctors
- Mysuru
-

Bengaluru

-

Bhubaneswar
-

Delhi - NCR

-

Delhi - NCR
-
-

Goa
-

Jaipur
-

Kolkata

-

Mangaluru
-

Mysuru
-

Patiala
-

Pune

-

Salem
-

Vijayawada
- International Patients










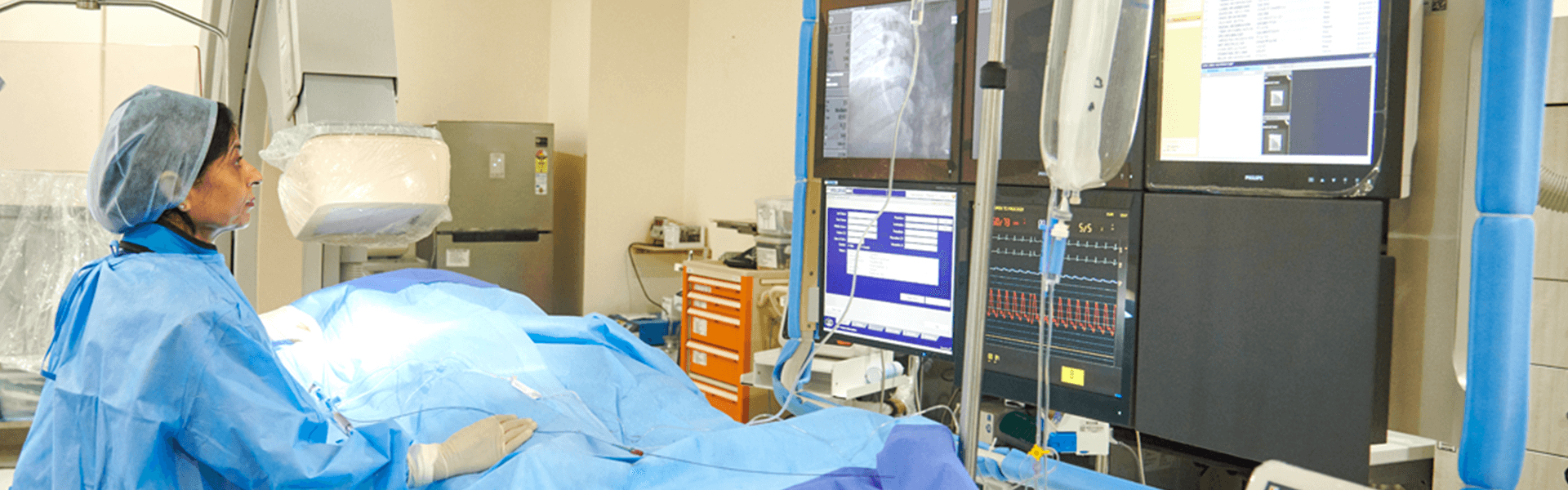
Echocardiogram (Echo)
Echocardiogram Treatment in Mysore
Cardiac Echo, Echocardiogram or Echo is the “Ultrasound of the Heart”. Here, the Echocardiography imaging test is performed to obtain live images of the patient’s heart; these live images are called Echocardiograms. The echo test uses sound waves to produce the heart's images, structure and function. Unlike X-rays and CT scans that use small radiation levels, Echo does not use radiation, making it different from other imaging facilities. Book an appointment to have the best treatment.
Why is Echo performed?
An echo test detects various heart diseases and heart-related medical conditions. Doctors usually recommend Echo when symptoms related to heart disorders are seen in patients or to detect likely ANT disorders. The results of Echo show any blood clots formed in the heart area or cardiac tumours. Generally, Echo is performed to detect various heart conditions and other disorders such as:
-
Congenital heart disease
-
Heart failure
-
Cardiac tumour
-
Aneurysm
-
Atrial and septal wall defects
-
Heart valve disease
-
Pericardial effusion
-
Infective endocarditis
-
Cardiomyopathy
Emergency Echocardiography
Patients in emergency conditions or accidents are scanned to detect any internal injuries. Echo is performed by a cardiac sonographer on patients suffering from emergency conditions such as chest pain, cardiac arrest, stroke, heart attack, breathlessness, undifferentiated shock, etc. Emergency Echocardiography is the cardiac ultrasound performed in the Emergency Room (ER) by ED specialists. Emergency Echo is immediately performed without any delay to address the time-sensitive and critical condition of the ill patient. ED healthcare providers use the Emergency Echo results to achieve the proper treatment or diagnostic interventions for a critical patient. Visit our emergency care hospital in Mysore for the best treatment.
Types of Echo
The echo test uses a similar technology to view an unborn child inside the pregnant woman. Now there are various types of Echocardiography, as follows:
-
Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): The traditional and most widely used Echo test is the Transthoracic Echo. This Echo test is Non-invasive, where no medical instruments are placed into the body. A transducer is placed on the patient’s chest, which sends ultrasound waves through the chest to the heart.
-
Transoesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): Here, images of heart areas like the aorta and other parts of the heart are taken from within the oesophagus with the help of a flexible tube.
-
Stress Echocardiography: This stress echo test is recommended to assess whether the heart is receiving enough oxygen and blood during its peak performance. A stress test is performed where the patient is made to exercise on the treadmill to compare the pictures of the heart before and after Echo. This is often used to detect coronary artery disease or heart attacks.
-
3D Echocardiography: Most detailed images of the heart are provided by the 3D Echo test. TEE and Intracardiac Echocardiogram (ICE) provide more detailed images than a traditional echo.
-
Foetal Echocardiography: As the name suggests, Foetal Echo is used to study an unborn child’s heart for any congenital or likely heart disorders.
Echo Procedure
-
In the traditional transthoracic echo test, sticky patches are attached to the patient’s chest to detect and conduct the heart’s electrical currents.
-
A gel is applied to the transducer to improve the conduction of the sound waves.
-
The transducer is now moved back and forth where the images of the heart’s sound-wave echoes are recorded.
-
However, in the transoesophageal echo, the patient’s throat is numbed by spray or gel, followed by a sedative to relax the patient. A flexible tube with a transducer attached to its end is placed down the food pipe, where heart images are taken.
-
This Echo procedure may take around an hour or less
Echo Results
The Echo results are considered normal and safe when Atrial or Septal walls are less than 1.5 cm thick and cardiac output (blood pumped per minute) is 4.8 to 6.5 litres when the body is resting. The alternative results to the above limits are considered abnormal, and your doctor recommends immediate diagnostic intervention.
Home Mysore Specialities Accident-and-emergency-care Echocardiogram-echo





