
Hearing the term “brain stroke” can be alarming, and it's natural to feel concerned. However, with a proper understanding of the condition, you can take steps to manage it. You need to know that high blood pressure (HBP) is the leading cause of brain strokes. HBP directly influences the health and stability of blood vessels in your brain. Consistent elevated blood pressure strains arteries. This makes them more prone to damage, narrowing, and ruptures. All of these contribute to increasing the risk of stroke. Let’s understand how to control high blood pressure effectively in detail in this blog.
Synopsis
Understanding High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is a measure of the force of blood against the walls of arteries as the heart pumps. It is represented by two values:
-
Systolic: Pressure during heartbeats
-
Diastolic: Pressure between heartbeats
Normal blood pressure is typically below 120/80 mmHg. High blood pressure, or hypertension, starts at 130/80 mmHg and above.
How Does High Blood Pressure Cause Stroke?
Both ischemic as well as hemorrhagic strokes can result from high BP. Let’s see how:
-
Ischemic stroke: It occurs when a blood clot obstructs blood flow to the brain. High blood pressure can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries (atherosclerosis), narrowing them and increasing the chances of clots forming and blocking blood flow.
-
Hemorrhagic Stroke: It occurs when blood vessels rupture in or near the brain. Chronic hypertension can weaken the walls of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to tearing under pressure, which leads to bleeding in the brain.
Signs and Symptoms of High Blood Pressure and Stroke:
It is absolutely critical to note that high blood pressure often shows no symptoms – thus, the name “Silent Killer” is commonly attributed to high blood pressure. However, as you can see, its effects can be dramatic.
In some cases, especially when blood pressure is dangerously high, you may experience:
-
Fatigue or confusion
-
Vision problems
-
Irregular heartbeat
-
Pounding in your chest, neck, or ears
Stay cautious with some generic signs to recognize stroke symptoms as early as possible for immediate intervention. Consult a neurologist today.
Below are the symptoms of stroke
-
Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, most commonly on one side of the body
-
Confusion or difficulty speaking or understanding speech
-
Trouble seeing in one or both eyes
-
Loss of balance or coordination, severe dizziness, or trouble walking
-
Severe headache with no known cause
Read our blog: How To Tell The Difference Between Stroke and Migraine?
Stroke Prevention with Blood Pressure Control
Did you know that stroke is the second leading cause of death in our country?
So, you can understand even if one feels the chills thinking about stroke, rarely do they take any preventive measures. Now, it is high time to take this seriously. Manage your blood pressure effectively to reduce the risk of stroke.
Here, we will shed light on some helpful stroke prevention tips:
-
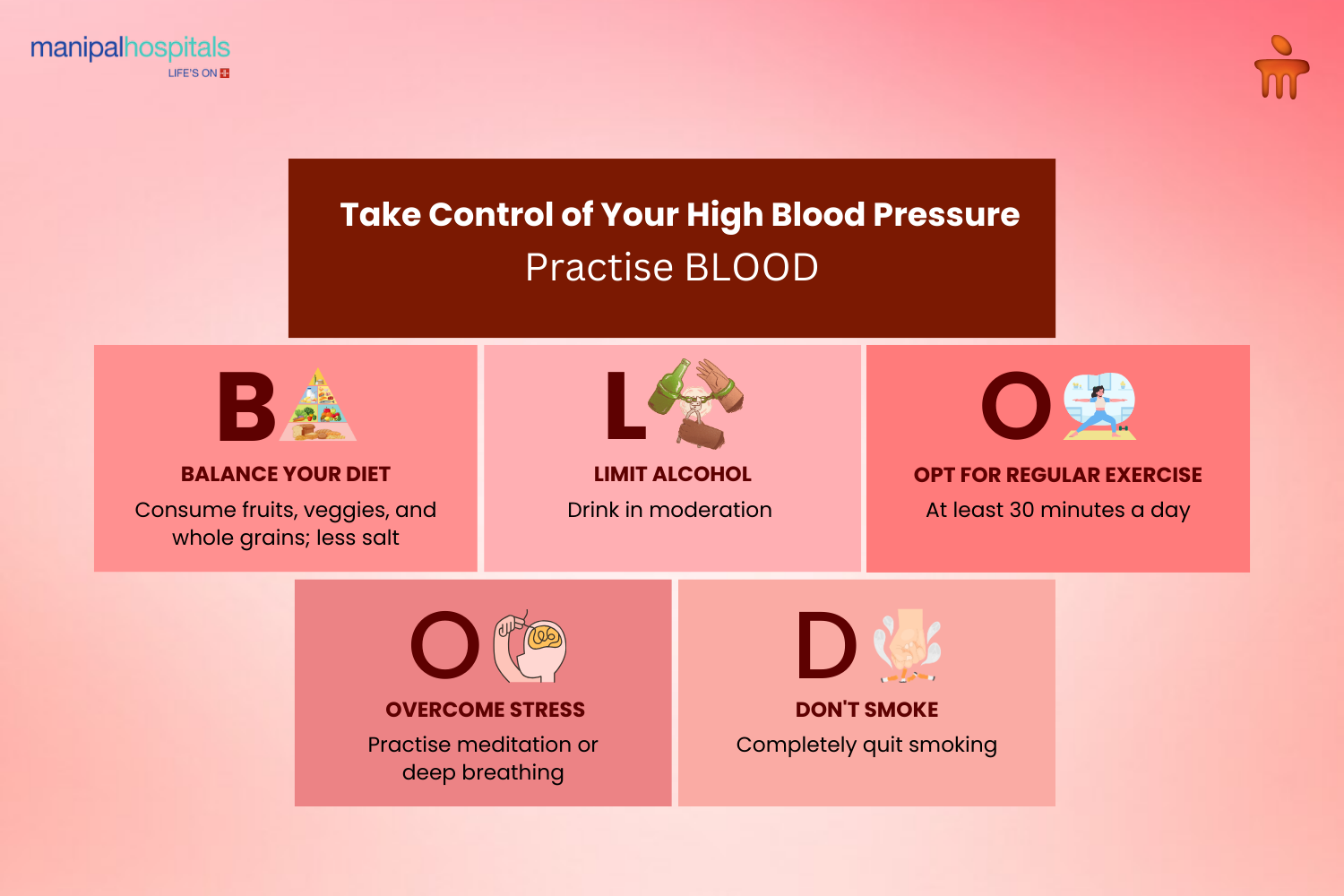
Regular Monitoring: Monitor your blood pressure regularly, especially if you’re at risk. Home monitoring devices can be helpful for these checks.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet low in salt, fat, and cholesterol and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains (such as the DASH diet) can help control blood pressure.
-
Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as 150 minutes of moderate weekly exercise, strengthens the heart and promotes better blood flow.
-
Medication: If prescribed, take blood pressure medications as directed. These can include diuretics, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and beta-blockers, which help reduce strain on arteries.
-
Limit Alcohol and Avoid Smoking: Alcohol and smoking both elevate blood pressure. Smoking cessation and limiting alcohol intake can boost blood vessel health and lower blood pressure.
-
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can also elevate blood pressure, so meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can support a healthy stress response and reduce hypertension.
Read our blog: Management of Stroke
Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Stroke Prevention
Long-term changes are the most crucial to prevent stroke. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, getting quality sleep, and managing chronic conditions like diabetes or high cholesterol.
If you have any questions or doubts, never think twice to consult with a healthcare professional. They can guide you with a personalized stroke-prevention plan based on your blood pressure readings. This tailored support is necessary for a more effective outcome.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is one of the most effective ways to prevent stroke. Understanding the relationship between blood pressure and stroke can empower you to take action in managing your overall health. Through regular monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and seeking medical guidance, you can significantly lower your risk and enhance your overall well-being.
FAQ's
High blood pressure damages arteries and makes them more prone to blockages and ruptures, both of which can cause stroke
In many cases, lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and stress management can allow you to manage blood pressure. However, some individuals may require medical management for optimal results.
A blood pressure level below 120/80 mmHg is ideal for most adults to minimize the risk of stroke and other BP complications.



















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read
















