Colorectal cancer is among the third most common cancers worldwide. In 2022, India reported 70,038 new cases of colorectal cancer and 40,993 deaths related to the disease. However, colon cancer can often be prevented and treated if detected early. People diagnosed in the early stages of the disease tend to have significantly higher survival rates. Regular screening is crucial to prevent colon cancer, and Colonoscopy is the gold standard for its early detection and treatment. In this blog, we will explore the Colonoscopy procedure and its importance in preventing colon cancer.
Synopsis
What is a Colonoscopy?
A Colonoscopy is a medical procedure used to examine the inside of the large intestine, including the colon, rectum, and anus. It’s an endoscopic procedure that uses a long, flexible tube called a colonoscope, which has a small camera attached to send live images of the inside of the large intestine to a monitor.
This helps doctors find polyps, abnormal growths, swollen or irritated tissues, or potential signs of cancer in the colon and rectum. Along with its diagnostic role, Colonoscopy can also be used for the removal of polyps or for collecting tissue samples for biopsy.
Colonoscopy Procedure
Pre-Procedure: Preparation for the Colonoscopy test is very important for the success of this procedure. You will get detailed instructions regarding bowel preparation (emptying the colon using laxatives or enema), diet (low-fibre or clear liquid diet), and medications (adjustments in regular medications) to follow before the procedure. This will help in getting a clean and clear view of the colon.
Procedure: It may take around 30-60 minutes for the procedure. You will be given sedation and pain medications through an IV line in your arm. Then the colonoscopy is gently inserted into your rectum and guided to reach the colon. The camera attached will keep sending real-time images to the monitor, helping the doctor inspect any abnormalities inside. The full colon till the end will be inspected. In case any polyps are found, they will be removed to prevent them from becoming cancerous. Tissue samples may also be taken for Biospy if needed.
Post-Procedure: You will be monitored in the recovery room till the effect of sedation wears off completely. Will be advised to avoid driving or making important decisions till the next day. You may feel some pain, nausea, or bloating, but it will pass away soon. Based on the findings, the doctor will recommend a follow-up for the next screening test.
|
Aspect |
Details |
|
Procedure |
Insertion of a long, flexible tube with a camera into the rectum to examine the colon. |
|
Purpose |
Detects and removes polyps, identifies abnormalities, and screens for colorectal cancer. |
|
Success Rate |
Associated with a 69% decrease in new cases of colorectal cancer and an 88% decrease in the risk of death from it. |
|
Preparation |
Requires bowel preparation, including a clear liquid diet and laxatives the day before. |
|
Duration |
Typically 30-60 minutes. |
|
Sedation |
Usually performed under sedation to ensure patient comfort. |
|
Recovery Time |
Patients can usually return to normal activities the next day. |
|
Risks |
Low risk of complications such as bleeding, perforation, or adverse reactions to sedation. |
|
Alternatives |
Faecal occult blood test (FOBT), faecal immunochemical test (FIT), and Cologuard (stool DNA test). |
|
Recommended Age |
Screening typically starts at age 45, earlier for those with higher risk factors. |
|
Frequency |
Every 10 years for average-risk individuals, more frequently for those at higher risk. |
Recommendations for Colonoscopy Screening
As Colonoscopy helps in early diagnosis and improves treatment outcomes for colon cancer, it is thus recommended for routine cancer screening. You must get a Colonoscopy for cancer screening done if:
-
Older than the age of 45 and haven’t had one before
-
Haven’t got one in the last 10 years
-
Have a family history of colorectal cancer
-
Had a tissue removed in your last Colonoscopy
-
Have an inherited disease (Lynch syndrome or familial adenomatous)
-
Have inflammatory bowel disease
Importance of Colonoscopy for Early Detection of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer is a deadly disease and often does not show symptoms until it progresses to an advanced stage. Thus, screening is essential for early detection and better treatment. There may be other screening methods available for colon cancer, but Colonoscopy is the most sensitive test for early detection of cancerous conditions and is mostly recommended by doctors.
Colonoscopy helps in the early detection of colon cancer in the following ways:
-
Detecting and removing polyps: Polyps are small growths on the inner lining of the colon, which can become cancerous if not removed timely. Thus, Colonoscopy helps in detecting polyps and removing them immediately, preventing colon cancer from developing. Even follow-up Colonoscopies are done to remove any additional polyps that may develop.
-
Finding cancer at an early stage: Colon cancer does not show symptoms at an early stage, but regular screenings help in detecting early signs of cancer such as abnormal tissue growths or suspicious changes. These are then treated in the early stages, increasing the 5-year survival rates to around 90%.
-
Reduces mortality rate: Many studies have shown that with regular Colonoscopy screening, the mortality rate of colon cancer has decreased. Detecting cancer in its early stages enhances treatment options and leads to better outcomes, improving the quality of life for patients.
-
Beneficial for high-risk individuals: People having a family history of colon cancer or suffering from inherited diseases or inflammatory bowel diseases are at a higher risk of developing colon cancer. Regular Colonoscopy screenings help in the early detection of cancer in high-risk individuals, offering better results than other screening methods.
Consult our gastroenterologist in Patiala if you need a colon cancer colonoscopy or need to know more about the benefits of colonoscopy.
Post-Colonoscopy Care Tips
-
Managing side effects: Offer guidance on handling common post-procedure side effects.
-
Diet and hydration: Recommend dietary and hydration practices for a quick recovery.
-
Activity restrictions: Advice on activities to avoid in the days following the procedure.
Consult our gastroenterology hospital in Patiala if you need Colon Cancer Screening.
Colonoscopy Alternatives with Comparison
-
Faecal Immunochemical Test (FIT): Non-invasive, detects blood in stool, but less comprehensive than colonoscopy.
-
Cologuard: Stool DNA test, non-invasive, but can miss some cancers.
-
Flexible sigmoidoscopy: Examines only the lower part of the colon, less thorough than a full colonoscopy.
-
Virtual colonoscopy: Uses CT scans, non-invasive, but requires follow-up colonoscopy if abnormalities are found.
-
Gold standard: Colonoscopy remains the most comprehensive and reliable screening method.
Conclusion
Colonoscopy is considered the gold standard for colon cancer screening as it provides a clear and direct view of the colon and rectum. In addition, polyps can be detected and removed before they become cancerous. It is also the most reliable method for colon cancer screening. While its preparation process may look challenging, its benefits in the early detection of cancer outweigh any discomfort associated with the procedure. For individuals aged 45 and above, or those with a higher risk, regular colonoscopy screenings can be life-saving. If you are due for a Colonoscopy, don't delay and schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Patiala, for better detection and treatment of colon cancer.
FAQ's
Although the procedure is done under sedation, you won’t feel any pain. But you might feel pressure or gas pain when the colonoscope is inserted.
Just like any other procedure, Colonoscopy carries some risks. These include injury to the colon wall, excessive bleeding, infection, and abnormal reactions to anaesthesia. These risks can be avoided if treated immediately and if an expert performs the procedure.
Alternative screening tests available for colon cancer are:
-
Faecal Occult Blood Test
-
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
-
Virtual Colonoscopy
-
Other stool tests
-
Digital Rectal Exam
-
Genetic Testing
If you are at a higher risk, get a screening done today from our experts.
Based on the results of your Colonoscopy, our doctor will recommend follow-up Colonoscopies. If you experience pain, swelling, a hardened belly, fever, frequent or bloody stools, or find it difficult to pass gas after the procedure, seek consultation with our doctor immediately.
You can schedule an appointment at Manipal Hospitals, Patiala, by contacting us or visiting our website.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read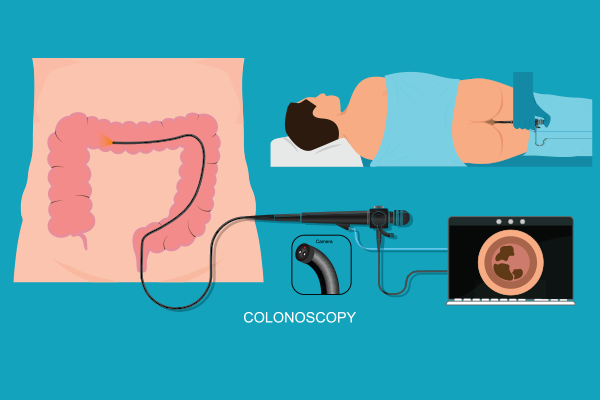







.png)