Gastroparesis is a chronic condition that affects the stomach muscles and prevents proper stomach emptying. This disorder can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, leading to various digestive symptoms and nutritional challenges. Understanding the Gastroparesis Symptoms, gastroparesis causes, signs of gastroparesis, and treatment options for gastroparesis is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Synopsis
Symptoms
The symptoms of gastroparesis can vary in severity and may include:
-
Nausea and Vomiting: One of the most common symptoms, often occurring after meals.
-
Early Satiety: Feeling full after eating only a small amount of food.
-
Bloating: A sensation of fullness or swelling in the abdomen.
-
Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the stomach area.
-
Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss due to reduced food intake and nutrient absorption.
-
Malnutrition: Resulting from poor nutrient absorption and inadequate dietary intake.
-
Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often related to acid reflux.
These symptoms can be intermittent or persistent, and their severity can fluctuate over time.
|
Diagnostic Method |
Description |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy (GES) |
Measures the rate at which food leaves the stomach using a radioactive tracer. |
Considered the gold standard; provides quantitative data on gastric emptying. |
Requires exposure to radiation; can be time-consuming and expensive. |
|
Breath Test |
Measures the rate of gastric emptying by analyzing breath samples after ingestion of a meal containing a non-radioactive isotope. |
Non-invasive; no radiation exposure. |
Less accurate than GES; influenced by other factors like lung function. |
|
SmartPill |
A capsule that measures pH, temperature, and pressure as it travels through the GI tract. |
Provides detailed information on GI motility; non-invasive. |
Expensive; not widely available; may not be suitable for all patients. |
|
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Endoscopy |
Visual examination of the stomach and duodenum using an endoscope. |
Can rule out mechanical obstructions; allows for biopsy if needed. |
Invasive; does not directly measure gastric emptying. |
|
Ultrasound |
Uses sound waves to create images of the stomach and assess its emptying. |
Non-invasive; no radiation exposure. |
Operator-dependent; less accurate for assessing gastric emptying. |
|
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) |
Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the stomach. |
Non-invasive; no radiation exposure; provides detailed images. |
Expensive; less accessible; may not be suitable for patients with metal implants. |
Consult our gastroenterologists in Patiala if you are experiencing Gastroparesis Symptoms.
Causes
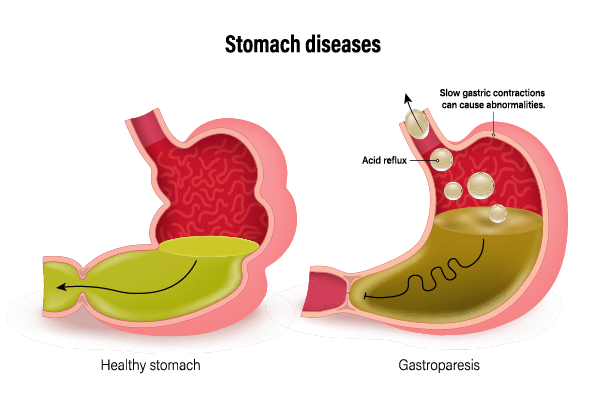
The exact cause of gastroparesis is often unknown, but several factors can contribute to its development:
-
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the vagus nerve, which controls stomach muscles.
-
Surgery: Operations on the stomach or other parts of the digestive tract can affect stomach nerves.
-
Medications: Certain drugs, such as narcotics and some antidepressants, can slow stomach emptying.
-
Viral Infections: Some viral infections can lead to temporary or permanent gastroparesis.
-
Neurological Disorders: Conditions like Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis can impact stomach motility.
-
Autoimmune Diseases: Disorders where the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues, including the stomach.
-
Idiopathic: In many cases, the cause remains unknown despite thorough investigation.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing gastroparesis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests:
-
Medical History and Physical Examination: A detailed history of symptoms and a physical exam to rule out other conditions.
-
Gastric Emptying Study: A test where the patient eats a meal containing a small amount of radioactive material, and the rate at which food leaves the stomach is measured.
-
Upper Endoscopy: A procedure using a flexible tube with a camera to examine the stomach and upper digestive tract.
-
Ultrasound: Imaging to rule out other causes of symptoms, such as gallbladder disease.
-
SmartPill: A capsule that measures pH, temperature, and pressure as it travels through the digestive tract.
-
Electrogastrography: A test that measures electrical activity in the stomach muscles.
Treatment
Treatment for gastroparesis aims to manage symptoms and improve stomach emptying. It often involves a combination of dietary changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions:
1. Dietary Modifications
Small, Frequent Meals: Eating smaller amounts more frequently can help manage symptoms.
-
Low-Fiber and Low-Fat Diet: Foods high in fiber and fat can slow stomach emptying.
-
Pureed or Liquid Foods: Easier to digest and pass through the stomach.
-
Avoid Carbonated Drinks: These can increase bloating and discomfort.
2. Medications
-
Prokinetics: Drugs like metoclopramide and erythromycin that stimulate stomach muscle contractions.
-
Antiemetics: Medications such as ondansetron to control nausea and vomiting.
-
Pain Management: Analgesics for abdominal pain, though narcotics should be avoided as they can worsen symptoms.
3. Surgical and Other Interventions
-
Gastric Electrical Stimulation: A device implanted in the stomach to stimulate muscle contractions.
-
Feeding Tubes: For severe cases, a feeding tube may be placed directly into the small intestine.
-
Parenteral Nutrition: Intravenous feeding for those who cannot tolerate any oral intake.
4. Alternative Therapies
-
Acupuncture: Some patients find relief through acupuncture treatments.
-
Biofeedback: Techniques to help manage symptoms through relaxation and stress reduction.
Consult our gastroenterology hospital in Patiala if you need Gastroparesis treatment.
Diet Tips for Gastroparesis
|
|
|
|
|
Chew food thoroughly and eat slowly. Avoid high-fat and high-fiber foods. Opt for low-residue and easily digestible foods. |
|
|
Sit upright or take a gentle walk after meals to aid digestion. |
|
|
Avoid carbonated beverages and alcohol. |
|
|
Avoid vigorous exercise immediately after meals. |
|
|
Ensure adequate sleep and manage stress effectively. |
|
|
Discuss any side effects or concerns with your doctor. |
Living with Gastroparesis
Managing gastroparesis requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized management plan. Support from dietitians, gastroenterologists, and patient support groups can also be invaluable.
Conclusion
Gastroparesis is a challenging condition that can significantly impact daily life. With the right diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan, many people can manage their symptoms well. This helps them maintain a good quality of life. Research is ongoing to improve our understanding of gastroparesis. We aim to develop better treatment options for those affected by this condition.
If you need expert care and treatment for gastroparesis, visit Manipal Hospitals Patiala. They have modern facilities and a skilled team of gastroenterologists. Manipal Hospitals Patiala focuses on patients. They are committed to giving you the best care for gastroparesis. Their goal is to help you manage your condition and improve your quality of life.
|
Myth |
Fact |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FAQ's
Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, early satiety, bloating, abdominal pain, weight loss, malnutrition, and heartburn.
Causes can include diabetes, surgery, medications, viral infections, neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, and idiopathic factors.
Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, gastric emptying studies, upper endoscopy, ultrasound, SmartPill, and electrogastrography
Medications include prokinetics, antiemetics, and pain management drugs, though narcotics should be avoided
Yes, options include gastric electrical stimulation, feeding tubes, and parenteral nutrition for severe cases.
Yes, lifestyle changes such as dietary adjustments, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritants can help manage symptoms.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read