
Paresthesia is a condition characterized by abnormal sensations such as tingling, numbness, or a "pins and needles" feeling, often in the hands, feet, arms, or legs. These sensations can be temporary or chronic and may result from various underlying causes. Understanding the paresthesia causes, paresthesia symptoms and paresthesia treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Synopsis
Paresthesia Causes
Paresthesia can arise from multiple factors, including nerve compression, circulatory issues, nutritional deficiencies, medical conditions, and injuries.
Nerve Compression
Nerve compression occurs when there is pressure on a nerve, which can disrupt its function and lead to paresthesia. Common scenarios include:
-
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the median nerve in the wrist.
-
Herniated Discs: Pressure on spinal nerves due to displaced vertebral discs.
-
Repetitive Strain Injuries: Frequent use of certain muscles leading to nerve compression.
Circulatory Issues
Poor blood circulation can deprive nerves of essential nutrients and oxygen, causing paresthesia. Conditions that can affect circulation include:
-
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Narrowing of arteries reduces blood flow to limbs.
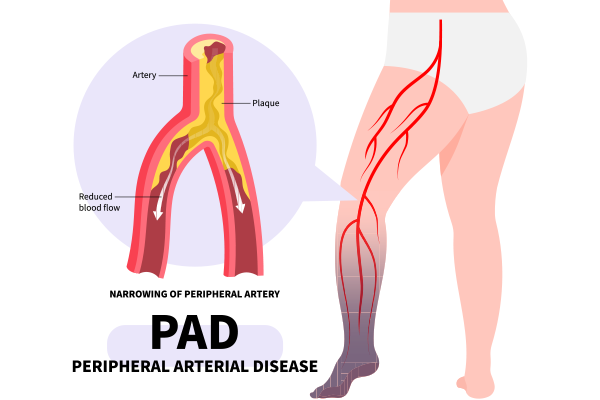
-
Raynaud's Disease: Spasms in blood vessels reduce blood flow to extremities.

Here's a table summarizing the causes, symptoms, and treatments for paresthesia:
|
Category |
Details |
|
Causes |
|
|
Symptoms |
|
|
Treatments |
|
Nutritional Deficiencies
Certain vitamins and minerals are vital for nerve health. Deficiencies can lead to nerve damage and paresthesia:
-
Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Essential for nerve function and myelin sheath maintenance.
-
Magnesium Deficiency: Important for nerve transmission and muscle function.
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can cause or exacerbate paresthesia:
-
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time (diabetic neuropathy).
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): An autoimmune disease that damages the protective covering of nerves.
-
Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism can lead to nerve damage and paresthesia.
Injuries
Physical trauma or repetitive strain injuries can damage nerves, leading to paresthesia:
-
Fractures: Broken bones can compress or sever nerves.
-
Sports Injuries: Repetitive motions or acute injuries in sports can affect nerves.
Paresthesia Symptoms
The symptoms of paresthesia can vary in intensity and duration, often depending on the underlying cause.
- Tingling Sensation
One of the most common symptoms is a tingling sensation, often described as "pins and needles." This can occur in any part of the body but is most frequently felt in the extremities.
- Numbness
Numbness is another prevalent symptom, where there is a loss of sensation in the affected area. This can make it difficult to feel touch, temperature, or pain.
- Burning or Prickling
Some individuals experience a burning or prickling sensation, which can be uncomfortable and persistent.
- Intermittent vs. Persistent Symptoms
Paresthesia can be intermittent, occurring sporadically, or persistent, where symptoms are continuous. Chronic paresthesia often indicates an underlying medical condition that requires attention.
- Affected Areas
Paresthesia commonly affects the hands, feet, arms, and legs. However, it can occur in other parts of the body, depending on the cause.
Paresthesia Treatment
Treatment for paresthesia focuses on addressing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can help reduce symptoms:
-
Posture and Ergonomics: Improving posture and using ergonomic tools can reduce nerve compression.
-
Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve circulation and nerve health.
Medications
Various medications can help manage symptoms:
-
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications can alleviate mild symptoms.
-
Anti-inflammatory Drugs: These can reduce inflammation and relieve pressure on nerves.
-
Prescription Medications: In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to manage chronic pain or underlying conditions.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be beneficial in managing paresthesia:
-
Exercises: Specific exercises can strengthen muscles and improve nerve function.
-
Therapies: Techniques such as massage, heat therapy, and electrical stimulation can provide relief.
Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve nerve compression or repair damaged nerves:
- Carpal Tunnel Release: Surgery to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
- Decompression Surgery: Procedures to alleviate pressure on spinal nerves.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies:
-
Acupuncture: Inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve symptoms
-
Chiropractic Care: Adjustments to the spine and joints to improve nerve function
-
Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs and supplements may support nerve health
Prevention of Paresthesia
Preventing paresthesia involves maintaining overall health and taking specific measures to protect nerve function.
-
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals supports nerve health. Foods high in vitamin B12, magnesium, and other nutrients are particularly beneficial.
-
Regular Exercise
Staying active helps improve circulation and prevent nerve compression. Incorporating a mix of aerobic, strength, and flexibility exercises can be effective.
-
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate symptoms of paresthesia. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
-
Ergonomics
Proper workplace ergonomics can prevent repetitive strain injuries. Using ergonomic chairs, keyboards, and other tools can reduce the risk of nerve compression.
-
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect and manage underlying conditions that may cause paresthesia. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing chronic symptoms.
Conclusion
Paresthesia is a condition with various causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Understanding these aspects can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. By addressing underlying causes, making lifestyle changes, and seeking appropriate medical care, it is possible to alleviate the discomfort associated with paresthesia.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of paresthesia, it's important to seek professional medical advice. Manipal Hospitals Patiala offers comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services for neurological conditions, including paresthesia. With a team of experienced neurologists and state-of-the-art facilities, Manipal Hospitals is dedicated to providing personalized care and effective treatment plans. Visit Manipal Hospitals to learn more and schedule an appointment today.
FAQ's
You should see a doctor if you experience persistent, severe, or worsening symptoms, or if paresthesia is accompanied by other concerning signs such as weakness, pain, or loss of function.
Yes, paresthesia can sometimes indicate serious conditions such as diabetes, multiple sclerosis, or nerve damage. It's important to seek medical advice if you experience persistent or severe symptoms.
Home remedies include maintaining good posture, using ergonomic tools, staying active, and ensuring a diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals. However, it's important to consult a healthcare provider for persistent symptoms.
Paresthesia can be temporary or chronic. Temporary paresthesia often resolves on its own, while chronic paresthesia may require medical treatment to address underlying causes.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and tests such as blood tests, nerve conduction studies, and imaging scans to identify underlying causes.



















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read
















