
Heart blockage, also known as coronary artery disease (CAD), is a serious condition that results from the narrowing or obstruction of the arteries supplying blood to the heart. It is one of the leading causes of heart attacks and cardiovascular complications worldwide. Understanding the key causes of the reason for heart blockage, its symptoms, and ways to manage it can help prevent severe health issues.
Synopsis
- What is Heart Blockage?
- What Causes Heart Block?
- What Are the Symptoms of Heart Block?
- What Are the Risk Factors for Heart Block?
- How to Check Heart Blockage at Home?
- Blood Test for Heart Blockage
- How to Detect Heart Blockage
- Heart Blockage Surgery
- Facing Heart Blockage? How to Manage it -
- Conclusion
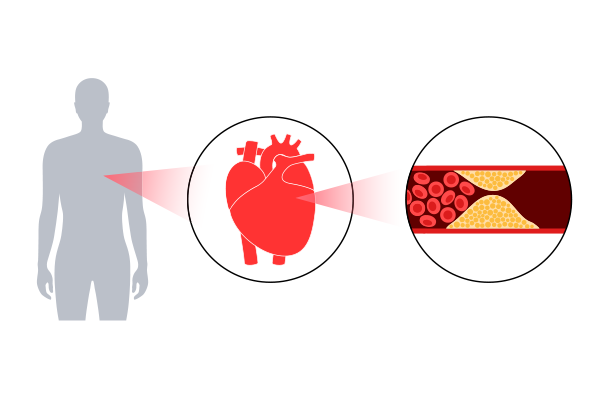
What is Heart Blockage?
Heart blockage occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or completely blocked due to plaque buildup. This restricts blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, and potential heart attacks.
What Causes Heart Block?
High Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol, a fatty substance in the blood, can accumulate in the arteries, leading to plaque formation. Over time, this buildup narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
High blood pressure exerts excess force on artery walls, causing damage and increasing the risk of plaque buildup, leading to blockages.
Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes leads to high blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels and promote atherosclerosis (hardening of arteries).
Smoking
Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that damage blood vessels, increase blood pressure, and promote plaque buildup.
Obesity
Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, increases the strain on the heart, raises cholesterol and blood pressure, and contributes to diabetes.
Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain, high cholesterol, and poor heart function, increasing the risk of blockages.
Poor Diet
A diet high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, and sugar leads to increased cholesterol, inflammation, and arterial plaque buildup.
Chronic Stress
Long-term stress triggers hormonal changes that increase blood pressure, heart rate, and inflammation, contributing to heart blockage.
Genetic Factors
A family history of heart disease increases the likelihood of developing arterial blockages due to inherited risk factors like high cholesterol or hypertension.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Drinking excessive alcohol can lead to high blood pressure, obesity, and increased triglyceride levels, all of which contribute to artery blockages.
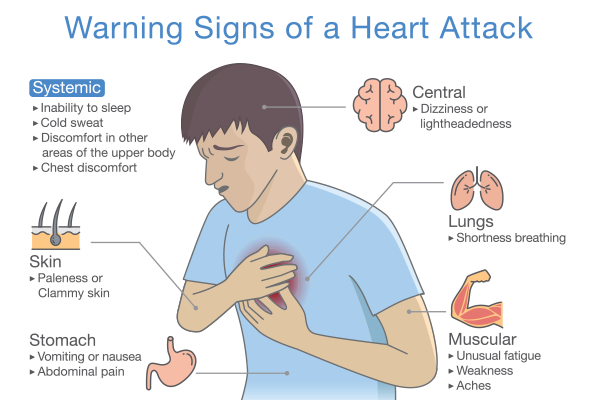
What Are the Symptoms of Heart Block?
-
Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
-
Shortness of breath
-
Fatigue and dizziness
-
Pain in the arms, neck, jaw, or back
What Are the Risk Factors for Heart Block?
-
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
-
Diabetes
-
Smoking and tobacco use
-
Obesity and lack of physical activity
-
Poor diet and high alcohol consumption
-
Chronic stress
-
Family history of heart disease
How to Check Heart Blockage at Home?
While a professional medical diagnosis is necessary, some warning signs can indicate heart blockage:
-
Monitor for persistent chest pain or discomfort.
-
Check for unusual shortness of breath during activities.
-
Observe sudden fatigue or dizziness.
-
Track irregular heartbeat patterns.
Blood Test for Heart Blockage
Doctors may recommend specific blood tests to assess heart health and detect potential blockages:
-
Lipid profile (to measure cholesterol levels)
-
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) test (to check inflammation)
-
Troponin test (to detect heart muscle damage)
-
NT-proBNP test (to assess heart failure risk)
How to Detect Heart Blockage
Medical tests used to diagnose heart blockage include:
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to monitor heart rhythms.
-
Stress test to observe heart function during exercise.
-
Echocardiogram to visualize heart structure and function.
-
Angiography to detect arterial blockages.
-
CT coronary angiogram for detailed artery imaging.
Heart Blockage Surgery
When lifestyle changes and medications are not sufficient, surgery may be necessary:
-
Angioplasty and Stenting: A catheter is used to open blocked arteries, often with a stent placement.
-
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Bypass surgery creates new pathways for blood flow.
-
Heart Transplant: In extreme cases, a transplant may be required.
More Reads: Common Heart Conditions Treated With Angioplasty
Facing Heart Blockage? How to Manage it -
|
Cause |
How It Leads to Heart Blockage |
How to Manage It |
|
High Cholesterol |
Cholesterol deposits form plaques that narrow arteries. |
Eat heart-healthy foods, exercise, and take prescribed medications. |
|
High Blood Pressure |
Damages artery walls, making them prone to blockages. |
Reduce salt intake, manage stress, and monitor BP regularly. |
|
Diabetes |
High blood sugar damages blood vessels, promoting plaque buildup. |
Control blood sugar through diet, exercise, and medications. |
|
Smoking |
Chemicals in tobacco damage arteries and increase clot risk. |
Quit smoking, seek support programs, and avoid secondhand smoke. |
|
Obesity |
Excess weight strains the heart and raises cholesterol and BP. |
Maintain a healthy weight through diet and regular exercise. |
|
Sedentary Lifestyle |
Lack of movement increases the risk of obesity and poor circulation. |
Engage in at least 30 minutes of physical activity daily. |
|
Poor Diet |
Processed foods and unhealthy fats contribute to plaque buildup. |
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. |
|
Chronic Stress |
Triggers hormonal changes that raise BP and inflammation. |
Practice relaxation techniques like meditation and deep breathing. |
|
Genetics |
Family history increases the likelihood of artery blockages. |
Get regular heart checkups and follow preventive measures. |
|
Excessive Alcohol |
Leads to high BP, obesity, and high triglycerides. |
Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels or avoid it. |
Conclusion
Heart blockage is preventable if the right lifestyle changes and medical interventions are followed. Managing cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and diabetes and adopting a healthy diet and active lifestyle can significantly lower the risk of heart disease. Awareness, early detection, and proactive management are key to maintaining a healthy heart and leading a long, fulfilling life.
If you are experiencing heart blockage symptoms or have concerns about your heart health, seeking professional medical advice is crucial. Manipal Hospital Patiala offers the best diagnostic and treatment options, including blood tests for heart blockage in Patiala, advanced imaging techniques, and heart blockage surgery in Patiala. Their expert cardiologists provide comprehensive care to help you maintain a healthy heart. Book an appointment today for an accurate assessment and personalized treatment plan.
FAQ's
Lifestyle changes, medications, and certain medical procedures can slow down or even partially reverse artery blockages.
High cholesterol levels and hypertension are the most common causes of heart blockage.
Procedures like angioplasty and bypass surgery are highly effective in restoring blood flow and preventing heart attacks.
While no home remedy can definitively diagnose heart blockage, monitoring symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and irregular heartbeat can help in early detection.
Doctors use ECG, stress tests, echocardiograms, angiography, and blood tests for heart blockage to diagnose artery blockages.
Yes, a completely blocked artery can lead to a heart attack or cardiac arrest, which can be fatal if not treated immediately.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read














