
Listen to article
Loading audio...
Rectal prolapse is a medical condition where the rectum, the final section of the large intestine, protrudes through the anus. This condition can be uncomfortable and distressing, but understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help manage and alleviate the condition effectively.
Synopsis
Rectal prolapse symptoms
The symptoms of rectal prolapse can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
-
Visible Protrusion: One of the most noticeable symptoms is a visible bulge or protrusion from the anus, especially during bowel movements.
-
Incontinence: Many individuals with rectal prolapse experience faecal incontinence, which is the inability to control bowel movements.
-
Mucus or Blood Discharge: There may be a discharge of mucus or blood from the protruding tissue.
-
Anal Itching and Irritation: The prolapsed tissue can cause itching and irritation around the anus.
-
Discomfort and Pain: Some people may experience discomfort or pain, particularly during bowel movements.
-
Feeling of Incomplete Evacuation: A sensation that the rectum is not completely empty after a bowel movement is common.
Causes of Rectal Prolapse
The exact cause of rectal prolapse is not always clear, but several factors can contribute to its development:
-
Chronic Constipation or Diarrhea: Persistent straining during bowel movements due to chronic constipation or diarrhoea can weaken the muscles supporting the rectum.
-
Ageing: As people age, the muscles and ligaments that support the rectum can weaken, increasing the risk of prolapse.
-
Pregnancy and Childbirth: The strain of pregnancy and childbirth can damage the pelvic floor muscles, leading to rectal prolapse.
-
Previous Pelvic Surgery: Surgeries involving the pelvic area can sometimes damage the muscles and tissues supporting the rectum.
-
Neurological Conditions: Conditions that affect the nerves controlling the pelvic floor muscles, such as multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries, can contribute to rectal prolapse.
-
Chronic Coughing: Chronic coughing from conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can increase abdominal pressure and strain the pelvic floor muscles.
-
Genetic Factors: A family history of rectal prolapse can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
Diagnosis of Rectal Prolapse
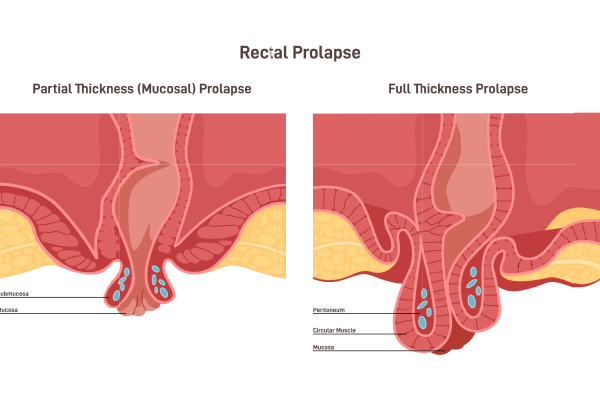
Diagnosing rectal prolapse typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
-
Patient History: A thorough medical history helps identify any underlying conditions or risk factors.
-
Physical Examination: A physical examination, including a rectal exam, allows the doctor to assess the extent of the prolapse.
-
Imaging Tests: Tests such as colonoscopy, defecography, and MRI can provide detailed images of the rectum and surrounding structures.
-
Manometry and Electromyography: These tests measure the strength and function of the anal sphincter muscles and pelvic floor.
Rectal prolapse treatment options
Treatment for rectal prolapse depends on the severity of the condition and the patient's overall health. Options range from lifestyle changes to surgical interventions:
Lifestyle Changes:
-
Dietary Adjustments: Increasing fibre intake and staying hydrated can help prevent constipation and reduce straining during bowel movements.
-
Pelvic Floor Exercises: Exercises like Kegels can strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and provide better support for the rectum.
-
Avoiding Strain: Avoiding heavy lifting and managing chronic cough can reduce abdominal pressure.
Medications:
-
Stool Softeners and Laxatives: These can help manage constipation and reduce straining.
-
Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments can alleviate symptoms like itching and irritation.
Non-Surgical Procedures:
-
Manual Reduction: In some cases, the prolapsed rectum can be manually pushed back into place.
-
Sclerotherapy: This involves injecting a solution into the rectal tissue to create scar tissue, which helps hold the rectum in place.
-
Surgical Treatments: Rectal prolapse surgery is often necessary for more severe cases of rectal prolapse. Common surgical options include:
-
Rectopexy: This procedure involves attaching the rectum to the sacrum (a bone in the lower back) to hold it in place.
-
Perineal Surgery: This approach involves removing the prolapsed section of the rectum through an incision in the perineum (the area between the anus and genitals).
-
Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive techniques using small incisions and a camera can be used to perform rectopexy or other repairs.
Common misconceptions about rectal prolapse
|
Myth |
Fact |
|
Rectal prolapse only occurs in older adults. |
Rectal prolapse can occur in people of all ages, including children and young adults. |
|
Surgery is the only treatment for rectal prolapse. |
There are non-surgical treatments available, such as pelvic floor exercises and lifestyle changes. |
|
Rectal prolapse is always painful. |
While it can cause discomfort, some people with rectal prolapse may not experience significant pain. |
|
Rectal prolapse is the same as haemorrhoids. |
Rectal prolapse and haemorrhoids are different conditions, though they may have similar symptoms. |
|
Only women get rectal prolapse. |
Both men and women can develop rectal prolapse, although it is more common in women. |
|
Rectal prolapse is caused by poor hygiene. |
Rectal prolapse is not related to hygiene; it is often due to weakened pelvic floor muscles or other medical conditions. |
Rectal Prolapse prevention and management
While not all cases of rectal prolapse can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
-
Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fibre helps prevent constipation and reduces straining during bowel movements.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water keeps stools soft and easier to pass.
-
Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity promotes healthy bowel function and strengthens the pelvic floor muscles.
-
Avoid Straining: Avoiding excessive straining during bowel movements and managing chronic cough can reduce abdominal pressure.
-
Pelvic Floor Exercises: Regularly performing pelvic floor exercises can strengthen the muscles supporting the rectum.
Complications of Untreated Rectal Prolapse
Untreated rectal prolapse can lead to several serious complications, which can significantly impact a person's health and quality of life. Here are some of the key complications:
- Ulceration and Bleeding
Chronic irritation of the prolapsed rectal tissue can lead to the development of ulcers. These ulcers can cause persistent bleeding, which may be noticeable during bowel movements or on toilet paper. The constant exposure of the rectal tissue to external elements can exacerbate irritation and ulceration, leading to discomfort and potential anaemia due to blood loss.
- Strangulation
Strangulation occurs when the blood supply to the prolapsed rectal tissue is compromised. This can happen if the prolapsed tissue becomes swollen and trapped outside the anus, cutting off its blood flow. Strangulation is a medical emergency as it can lead to tissue death (necrosis) and severe pain. Immediate medical intervention is required to restore blood flow and prevent further complications.
- Infection
The exposed rectal tissue is more susceptible to infections. The constant exposure to bacteria and other pathogens can lead to localized infections, which can cause pain, swelling, and discharge. In severe cases, the infection can spread to surrounding tissues and lead to more serious health issues, such as abscesses or systemic infections.
Addressing rectal prolapse promptly with appropriate medical treatment can help prevent these complications and improve overall outcomes. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of rectal prolapse, it is important to seek medical advice to avoid these potential complications.
Conclusion
Rectal prolapse is a condition that can significantly impact quality of life, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, symptoms can be managed effectively. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for those affected by this condition. If you suspect you have rectal prolapse, it is important to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. With the right approach, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
For those seeking expert medical care, Manipal Hospitals in Patiala offers comprehensive treatment options for rectal prolapse and other medical conditions. With state-of-the-art facilities and a team of highly skilled Gastrointestinal specialists and surgeons, Manipal Hospitals is dedicated to providing the best possible care to its patients. Whether you need a consultation or advanced surgical treatment, you can trust Manipal Hospitals Patiala to deliver exceptional healthcare services. Visit Manipal Hospitals Patiala to learn more and book an appointment.



















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read

















