
Imagine waking up one morning, unable to recall what you did yesterday or even where you left your phone just minutes ago. Memory Loss is the cornerstone of our daily lives, allowing us to function, recognise loved ones, and recall important events. But what happens when sudden memory loss disrupts this delicate balance? Short-term memory loss, where recent events fade away quickly, or more severe cases of amnesia, can be frightening. Understanding memory loss causes, recognising symptoms, and seeking appropriate memory loss treatment can make all the difference in restoring cognitive function. Let’s explore the various reasons behind sudden memory loss and how to manage it effectively.
Synopsis
Causes of Sudden Memory Loss
Medical Conditions
-
Stroke: A sudden stroke can restrict blood flow to parts of the brain responsible for memory, leading to memory loss.
-
Head Injury or Concussion: A severe blow to the head can damage brain structures, causing both short-term memory loss and long-term memory impairment.
-
Brain Infections: Conditions such as meningitis or encephalitis can lead to inflammation, damaging brain cells involved in memory processing.
-
Epileptic Seizures: Seizures disrupt normal brain activity, sometimes leading to temporary amnesia or confusion.
Neurological Disorders
-
Transient Global Amnesia (TGA): A rare condition where a person suddenly forgets recent events but retains knowledge of their identity.
-
Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: While gradual, certain forms of dementia can lead to episodes of sudden memory loss.
Psychological and Emotional Causes
-
Severe Stress or Trauma: High levels of stress or a traumatic event can lead to dissociative amnesia, where the brain blocks out painful memories.
-
Anxiety and Depression: These mental health conditions can affect concentration and recall, making it seem like memory loss.
Medication & Substance-Related Causes
-
Side Effects of Medications: Some prescription drugs, such as sedatives or antihistamines, can impair memory.
-
Alcohol or Drug Abuse: Excessive consumption of alcohol or certain drugs can interfere with memory formation and retrieval.
Other Contributing Factors
-
Sleep Deprivation: Chronic lack of sleep affects brain function, leading to short-term memory loss.
-
Vitamin Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients, especially Vitamin B12, can cause cognitive decline.
-
Thyroid Disorders: An underactive thyroid can lead to forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating.
Symptoms of Sudden Memory Loss
-
Difficulty recalling recent conversations or events.
-
Confusion and disorientation.
-
Forgetting familiar names, places, or routines.
-
Struggling to find words or express thoughts.
-
Sudden changes in mood or personality.
When to Seek Medical Help
Memory loss can sometimes be normal, but sudden and severe cases should never be ignored. If memory loss is accompanied by difficulty speaking, changes in coordination, or severe confusion, seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and memory loss treatment can prevent further complications.
Diagnosis & Tests for Sudden Memory Loss
-
Neurological Exams: Cognitive tests to assess brain function.
-
MRI or CT Scans: Imaging to detect structural damage or tumours.
-
Blood Tests: To identify infections, vitamin deficiencies, or metabolic issues.
-
EEG (Electroencephalogram): To detect abnormal brain activity in cases of seizures.
Interesting Facts About Memory Loss
|
Fact |
Explanation |
|
The brain can store 2.5 petabytes of information |
Equivalent to nearly 3 million hours of TV shows |
|
Sleep strengthens memory |
Deep sleep plays a crucial role in consolidating and storing memories. |
|
Stress can shrink the brain |
Chronic stress leads to the shrinking of the hippocampus, affecting memory retention. |
|
Your brain starts forgetting in seconds |
Without reinforcement, short-term memories fade quickly, sometimes within 15–30 seconds. |
|
Walking backwards can help recall memories |
Some studies suggest that physically moving backwards can trigger forgotten details. |
Treatment Options for Sudden Memory Loss
Medical Treatments
-
Addressing Underlying Conditions: If the memory loss causes include a stroke, infection, or thyroid disorder, treating the root issue can help restore memory.
-
Medications: In some cases, drugs to manage Alzheimer’s or cognitive disorders may be prescribed.
-
Cognitive Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises are designed to strengthen memory function.
Lifestyle Changes & Management
-
Memory Exercises: Activities like puzzles, reading, and meditation can boost cognitive health.
-
Balanced Diet: Consuming brain-healthy foods such as leafy greens, nuts, and omega-3-rich fish.
-
Stress Management: Practising mindfulness and relaxation techniques to reduce cognitive strain.
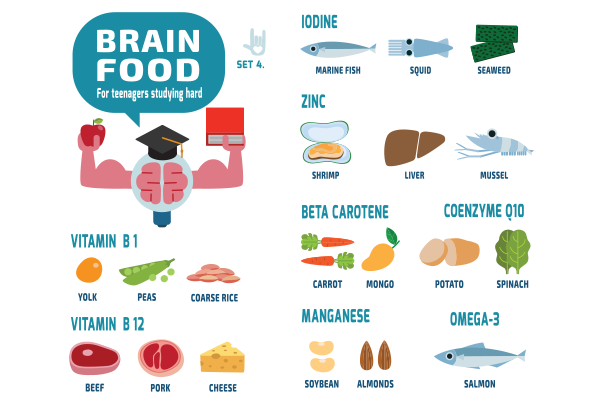
Preventing Memory Loss
-
Stay mentally active by engaging in new learning activities.
-
Get enough sleep to support cognitive processing.
-
Exercise regularly to improve blood flow to the brain.
-
Avoid excessive alcohol and drug use.
-
Schedule routine health check-ups to monitor conditions affecting brain health.
Conclusion
Memory loss can be alarming, but early diagnosis and appropriate memory loss treatment can significantly improve cognitive function. If you or a loved one experiences persistent short-term memory loss, seeking expert medical care is essential. At Manipal Hospital Patiala, our team of neurologists and specialists provides comprehensive diagnostic and treatment solutions tailored to your needs. We are committed to helping patients regain their cognitive abilities and improve their quality of life. Book an appointment today and take the first step toward a healthier brain.
FAQ's
In many cases, yes. If caused by stress, sleep deprivation, or vitamin deficiencies, memory loss can improve with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. However, conditions like Alzheimer’s require long-term management.
It depends on the memory loss. Some cases, like TGA, resolve within 24 hours, while others may persist if linked to neurological conditions.
Yes, extreme stress and trauma can temporarily block memory recall, leading to dissociative amnesia.
Persistent forgetfulness, difficulty in recognising familiar faces or places, and confusion should be taken seriously. Seeking memory loss treatment early can help prevent worsening conditions.
Engage in brain-stimulating activities, maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and get adequate sleep to enhance memory retention.



















 5 Min Read
5 Min Read


















