
Brain hemorrhage is a medical emergency that can result in serious and life-threatening consequences. Bleeding in or around the brain puts pressure on brain tissue and interferes with normal brain function. A brain hemorrhage is associated with high mortality rates, especially if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
In this blog, we will disclose when brain hemorrhages happen, the causes, symptoms, and treatments of this condition, and how you can recognise them.
Synopsis
What is Brain Hemorrhage?
A brain hemorrhage (brain bleed or intracranial hemorrhage) is a type of stroke in which a blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing bleeding inside the brain. It can bleed in and on the brain or the surrounding spaces.
This causes blood to pool and create pressure on brain cells, causing damage and disrupting normal brain function. In addition, it presses so hard that it leads to serious complications, including paralysis or death, or disturbances of the brain’s control of body functions, including cognitive impairments.
Know the Brain Hemorrhage Causes
Brain hemorrhages can result from several conditions. The most common causes of brain hemorrhage include:
-
High Blood Pressure: Chronic hypertension causes brain hemorrhage. This condition affects blood vessels, and the raised pressure weakens their walls over time.
-
Aneurysms: An aneurysm is a weakened area of a blood vessel wall that bulges out. They are a type of brain hemorrhage that occurs when one of these pockets balloons and bursts.
-
Trauma or Injury: A type of brain injury, such as a car accident or fall, causes a brain hemorrhage. A rupture of blood vessels in the brain can occur as a result of trauma.
-
Blood Clotting Disorders: Conditions that interfere with blood clotting, such as haemophilia or anticoagulants (blood thinners), increase the risk of brain hemorrhage. If you have these conditions, you can bleed into the brain more quickly because the blood won’t clot properly.
-
Brain Tumours: A brain tumour can also cause hemorrhaging if pressure on blood vessels in the brain causes them to burst.
-
Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy: This occurs when amyloid proteins accumulate in the walls of the brain's blood vessels, making them weak and prone to rupture.
-
Drug Use: Brain hemorrhage may also be caused by some drugs taken recreationally (e.g., cocaine or methamphetamines) by altering the pressure or integrity of blood vessels.
-
Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): Brain tangles of abnormal blood vessels that can break and bleed.
Brain Hemorrhage Symptoms
Recognising brain hemorrhage symptoms early is crucial to reducing the risk of long-term damage or death. The signs of brain hemorrhage can vary depending on the location and size of the bleeding, but common brain hemorrhage signs and symptoms include:
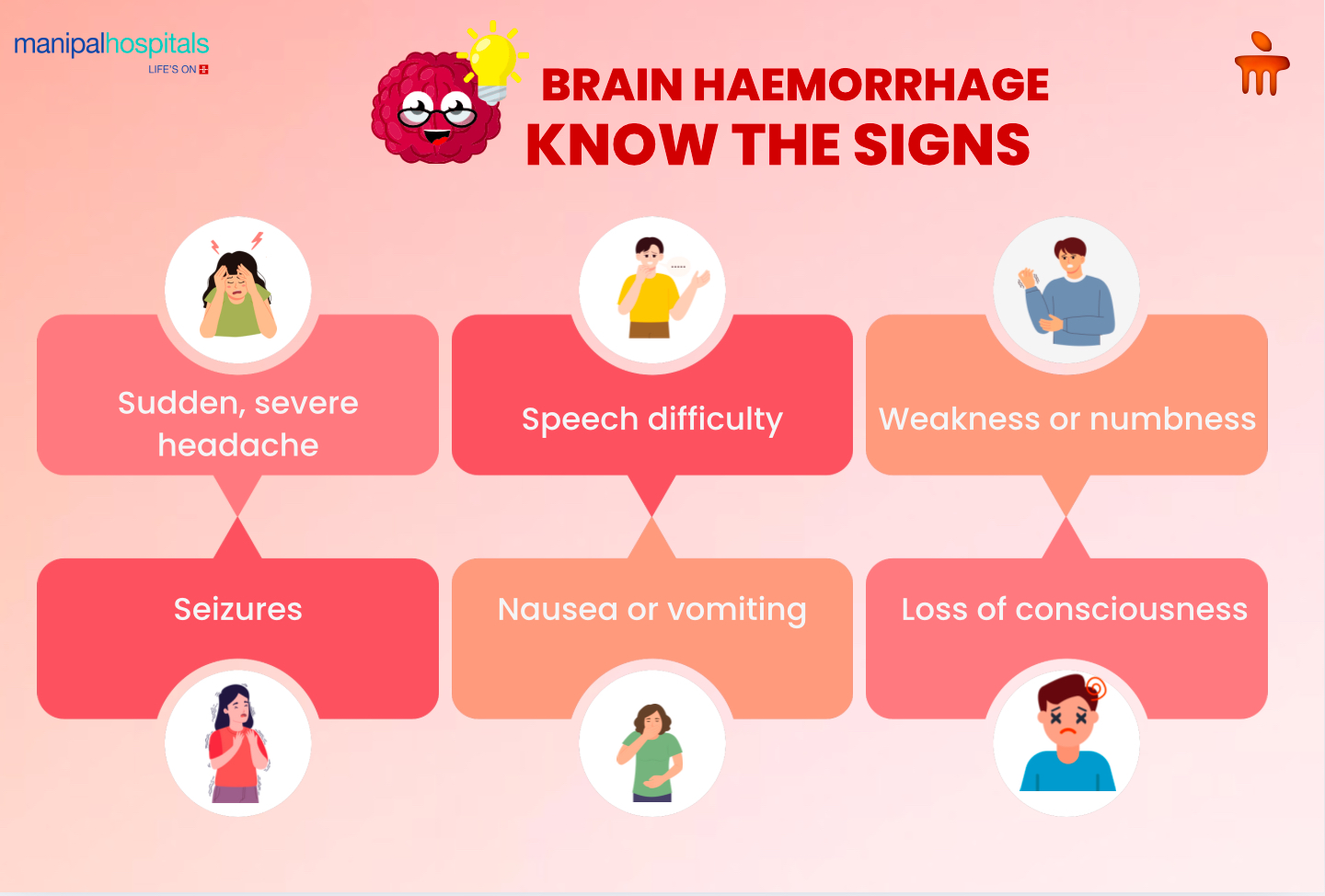
-
Sudden Severe Headache: One of the most prominent symptoms of brain hemorrhage is a sudden, severe headache, often described as the worst headache a person has ever experienced.
-
Nausea and Vomiting: Along with the headache, a person experiencing a brain hemorrhage may feel nauseous and may vomit.
-
Loss of Consciousness: In severe cases, the individual may lose consciousness or experience confusion, disorientation, or difficulty speaking clearly.
-
Weakness or Numbness: A person may experience weakness or numbness on one side of the body, especially in the arms or legs. This indicates damage to the brain's area that controls motor functions.
-
Vision Problems: If a brain hemorrhage affects the areas of the brain responsible for vision, blurred or double vision can occur.
-
Seizures: A brain hemorrhage can disrupt electrical activity in the brain, leading to seizures or convulsions.
-
Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing: As pressure increases in the brain, it may affect the brain's control over vital functions such as breathing or swallowing.
-
Speech Difficulties: Difficulty speaking or understanding speech can also be a sign that a brain hemorrhage has occurred.
Diagnosing Brain Hemorrhage
If a brain hemorrhage is suspected, immediate medical attention is required. Diagnostic tests, such as CT scan, MRI scan, angiogram, or spinal tap, are used to confirm brain bleed and determine the condition's severity. Blood tests may also be conducted to check for blood clotting disorders or other underlying conditions.
How to Treat Brain Hemorrhage?
The treatment for brain hemorrhage depends on the location, size, and cause of the bleeding. An immediate intervention is crucial for improving outcomes and minimising brain damage. Some treatment options for brain hemorrhage include:
Emergency Care:
The first step in treating a brain hemorrhage is stabilise the patient. This may involve administering oxygen, controlling blood pressure, and ensuring a clear airway. Patients may also be closely monitored in an intensive care unit (ICU).
Surgery:
In cases where the bleeding is extensive or the pressure in the brain is rising rapidly, surgery may be required. Surgery aims to remove blood clots, repair ruptured blood vessels, or relieve pressure on the brain. Procedures like craniotomy or endovascular coiling are sometimes used to treat brain hemorrhages. You can schedule a consultation with a neurosurgeon in Salem.
Medications:
Medications may be given to reduce brain swelling and prevent further complications, such as seizures. Blood pressure medications can help control hypertension, which is often a major cause of brain hemorrhages.
Rehabilitation:
After the acute phase of treatment, rehabilitation is often necessary to help patients recover lost brain function. This can include physical, occupational, and speech therapy to address weakness, speech issues, or cognitive impairments caused by the hemorrhage.
Read our blog: An Overview Of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Prevention of Brain Hemorrhage
While not all brain hemorrhages can be prevented, specific lifestyle changes and medical interventions can help reduce the risk. Controlling blood pressure, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, not smoking, and wearing protective gear during activities that could cause head injury (such as sports or riding a bike) can all lower the likelihood of a brain hemorrhage.
Managing conditions like aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations with medical treatment may also reduce the risk of future brain bleeding.
Conclusion
Brain hemorrhage is a serious medical condition that can lead to severe consequences if not addressed promptly. Understanding the causes, recognising brain hemorrhage symptoms, and seeking immediate treatment are essential for improving outcomes.
If you or someone you know exhibits brain hemorrhage symptoms, visit Manipal Hospital Salem and seek emergency medical treatment without delay.
FAQ's
Several factors, including high blood pressure, aneurysms, trauma, blood clotting disorders, and brain tumours, can cause brain hemorrhages. These conditions weaken blood vessels in the brain, making them more susceptible to rupture.
Common symptoms include sudden severe headache, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, weakness or numbness on one side of the body, vision problems, and speech difficulties. Seek immediate medical help if these symptoms occur.
Treatment may involve emergency care to stabilize the patient, medications to control symptoms, surgery to remove clots or relieve pressure, and rehabilitation to help recover lost brain function.
To lower the risk of brain hemorrhage naturally, you can:
-
Control Blood Pressure: Reduce salt intake and consume potassium-rich foods like bananas and spinach.
-
Improve Blood Clotting Naturally: Eat foods rich in vitamin K (leafy greens) to support blood clotting and prevent excessive bleeding.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water keeps blood circulation smooth.
-
Avoid Alcohol & Smoking: Both weaken blood vessels and increase hemorrhage risk.
No, a brain hemorrhage is a medical emergency that requires immediate professional treatment. However, home remedies can help in prevention by maintaining healthy blood pressure, avoiding blood-thinning substances, and following a balanced diet to support brain and vascular health.
No, if a blood clot forms in the brain, it requires medical intervention. However, foods like turmeric, ginger, and garlic have mild anti-clotting properties that may support heart and brain health. Always consult a doctor before using any natural remedy for clot-related conditions.



















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read





.png)







