
Listen to article
Loading audio...
Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic disease that affects millions worldwide. This condition arises when the body is unable to effectively regulate blood sugar levels. This leads to high average blood sugar levels. If left untreated, this can cause serious health complications.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, types, and treatment of diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Let’s explore Diabetes Mellitus, everything you need to know for managing this condition.
Synopsis
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes Mellitus is a condition in which the body either does not produce insulin or cannot use it effectively. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels and facilitates the absorption of sugar by cells for energy.
Without enough insulin, sugar builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can damage the heart, kidneys, nerves, and eyes.
There are different types of diabetes, each with distinct causes and treatments. However, they all lead to a common issue: unhealthy blood glucose levels.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
There are four main types of diabetes, each with different causes and treatments.
1. Type 1 Diabetes
This autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This primarily affects children and young adults.
-
Requires lifelong insulin therapy
-
Symptoms develop quickly
-
Cannot be prevented
2. Type 2 Diabetes
This is the most common type of diabetes. It happens when the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough of it.
-
Mostly affects adults, but cases in young people are rising.
-
Associated with obesity, unhealthy diet, and lack of activity.
-
It can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs mostly during pregnancy because of hormonal changes. This affects insulin function.
-
Usually resolves after childbirth
-
Increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes in the future
-
Managed through diet and exercise
4. Prediabetes
This is a warning stage where blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis.
-
Normal blood sugar levels range from 70-99 mg/dL
-
Prediabetes range: 100-125 mg/dL
-
This can be reversed with a balanced diet and regular exercise
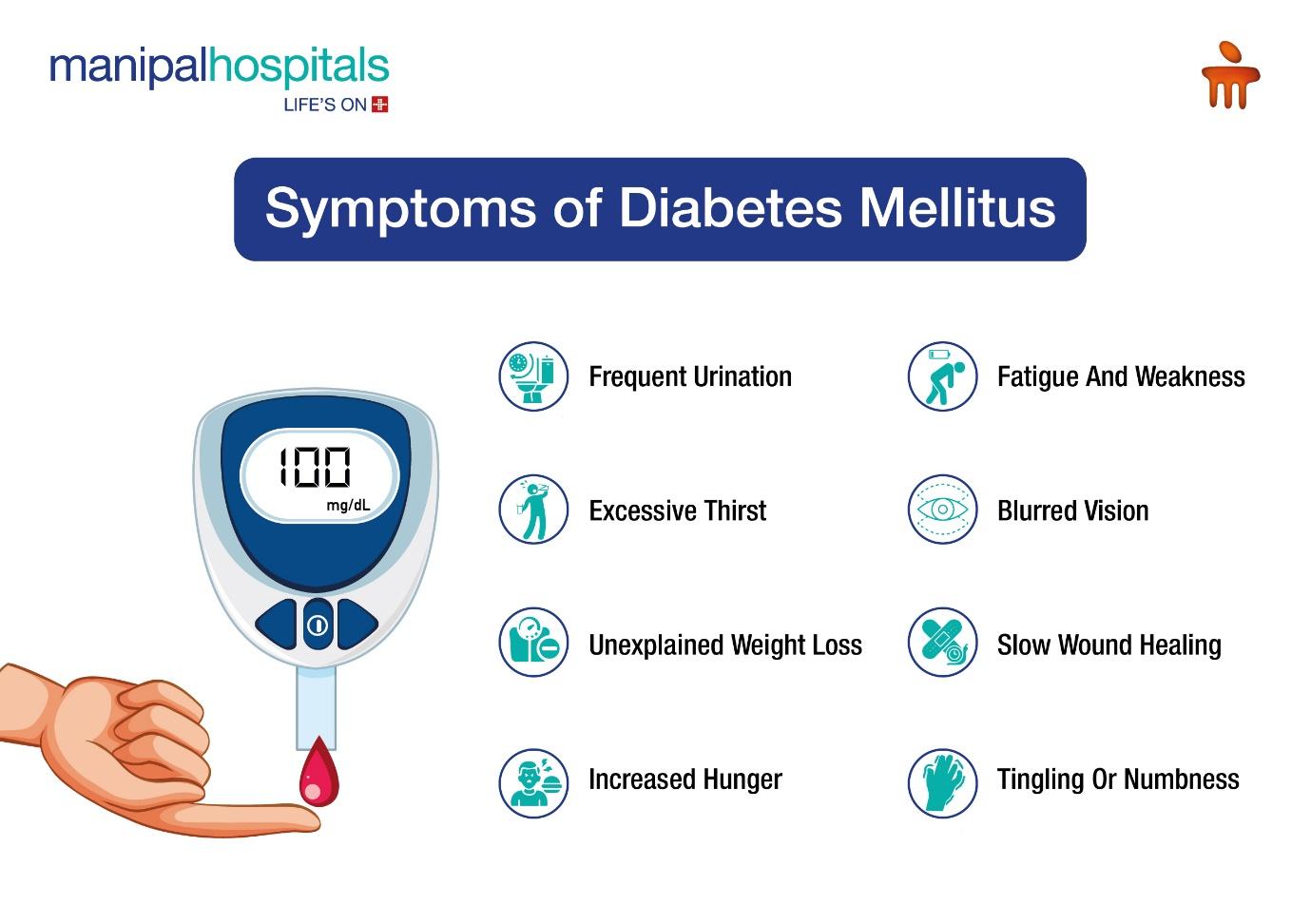
What are the Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes symptoms can develop slowly, especially in Type 2 diabetes. Some people may not notice any signs until complications arise. Common symptoms include:
-
Frequent urination: The kidneys try to remove excess sugar from the body.
-
Excessive thirst: Due to frequent urination.
-
Unexplained weight loss: The body burns fat for energy due to a lack of insulin.
-
Increased hunger: Cells do not get enough glucose, leading to constant hunger.
-
Fatigue and weakness: Lack of sugar in the cells causes low energy.
-
Blurred vision: Eyes blood vessels can be damaged due to high blood glucose levels.
-
Slow wound healing: High sugar affects circulation and immune function.
-
Tingling or numbness: Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy) can cause this.
Note: If you notice these symptoms, consult a doctor immediately for blood sugar testing.
Causes of Diabetes Mellitus
The exact causes of diabetes vary by type, condition. However, the most common risk factors include:
-
Genetics: Family history increases the risk.
-
Obesity: Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can cause insulin resistance.
-
Unhealthy Diet: High consumption of processed foods and sugary drinks can contribute.
-
Lack of Exercise: A sedentary lifestyle affects insulin sensitivity.
-
Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like PCOS and thyroid disorders can increase risk.
Other factors like stress, infections, and certain medications may also trigger diabetes.
Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus
Doctors use different tests to check blood glucose levels and confirm diabetes.
|
Test Name |
Purpose |
Normal Blood Sugar Levels |
Diabetes Range |
|
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) |
Measures sugar levels in blood after 8 hours of fasting |
Below 100 mg/dL |
126 mg/dL or higher |
|
Random Blood Sugar Test |
Checks sugar levels at any time of the day |
Below 140 mg/dL |
200 mg/dL or higher |
|
HbA1c Test |
Shows average blood sugar level over 2-3 months |
Below 5.7% |
6.5% or higher |
Endocrinologists may also perform additional tests, such as oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) and insulin level tests, for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment for Diabetes Mellitus
Managing diabetes mellitus involves a combination of lifestyle improvement, medication, and regular monitoring.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making healthier choices can help control blood glucose levels naturally.
-
Healthy Diet: Eat whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and avoid sugar, oil & fatty foods
-
Regular Exercise: 30 minutes of walking or activity daily helps insulin work better.
-
Weight Management: Losing even 5-10% of body weight improves insulin sensitivity.
-
Quit Smoking & Alcohol: Smoking worsens diabetes complications.
Medications & Insulin Therapy
-
Oral Medications: Typically used for Type 2 diabetes to help regulate insulin.
-
Insulin Injections: Essential for Type 1 diabetes and severe Type 2 cases.
-
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Tracks blood sugar levels in real-time.
How to Prevent Diabetes Mellitus?
While Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, you can reduce the risk of Type 2 diabetes with these steps:
-
Eat a balanced diet, avoid processed foods and sugar.
-
Stay physically active and do regular exercise to improve insulin sensitivity.
-
Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity is a major risk factor.
-
Get regular health check-ups. Early detection prevents complications.
Taking these steps can help maintain healthy blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of diabetes.
Conclusion
Diabetes Mellitus is a serious yet manageable condition. Early diagnosis and proper management can prevent complications like heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. If you experience symptoms, get your blood sugar levels checked immediately. With the right lifestyle, medication, and care, you can live a healthy life despite diabetes. Book an appointment today at Manipal Hospitals for Diabetes Treatment in Kolkata.
FAQ's
The early signs of Diabetes Mellitus include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, and constant fatigue. Many people also experience blurry vision, slow-healing wounds, and a tingling sensation in their hands or feet.
Normal blood sugar levels vary based on the time of measurement. A fasting blood sugar level should be below 100 mg/dL, while post-meal blood sugar should be below 140 mg/dL.
Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes can sometimes be reversed with lifestyle changes. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight loss can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. However, Type 1 diabetes cannot be reversed and requires insulin therapy for life.
To maintain healthy blood glucose levels, it is essential to follow a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and monitor blood sugar levels consistently. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can also help stabilise glucose levels.
Yes, diabetes can be hereditary, especially Type 2 diabetes. If a close family member has diabetes, there is a higher risk of developing the condition. However, lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise play a significant role in either preventing or delaying the onset of diabetes.
Yes, chronic stress can increase blood glucose levels. When the body is under stress, it releases hormones that raise blood sugar. Managing stress through meditation, exercise, and adequate sleep can help keep glucose levels in check.
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on the type of diabetes and treatment plan. People with Type 1 diabetes usually need to check their blood sugar four to six times a day. Those with Type 2 diabetes who take insulin may check their levels three times a day, while those managing diabetes with lifestyle changes may only need to test once or twice a week.
If left uncontrolled, diabetes can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. High blood sugar levels over time can also increase the risk of stroke and slow down wound healing, increasing the chances of infections.



















 7 Min Read
7 Min Read












