Heatstroke, also known as sunstroke is a severe medical condition characterised by a rapid rise in core body temperature and impaired ability to sweat. This dangerous situation can quickly damage vital organs and even lead to death if not treated promptly.
While enjoying outdoor activities and soaking up the sun is part of summertime pleasures, understanding the risks and symptoms of heatstroke is crucial for ensuring your safety and well-being.
Synopsis
What exactly is Heatstroke?
Heatstroke causes occurs when the body's core temperature rises to dangerous levels, typically exceeding 104°F (40°C). It arises due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures or physical exertion in hot conditions. The body's cooling mechanisms, such as sweating, may fail, leading to a rapid increase in core body temperature and the onset of heatstroke.
Possible Causes of Heatstroke
While scorching temperatures are the primary culprit, several factors can fan the flames:
-
Strenuous Activity: Exercising or exerting yourself in hot environments significantly increases heat production.
-
Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake disrupts the body's cooling mechanism.
-
Certain Medications: Some medications can impair sweating or heat regulation.
-
Medical Conditions: Obesity, heart disease, and chronic illnesses can increase vulnerability.
-
Age: Infants, young children, elderly people and those with chronic conditions, such as heart disease or diabetics are at higher risk of heatstroke.
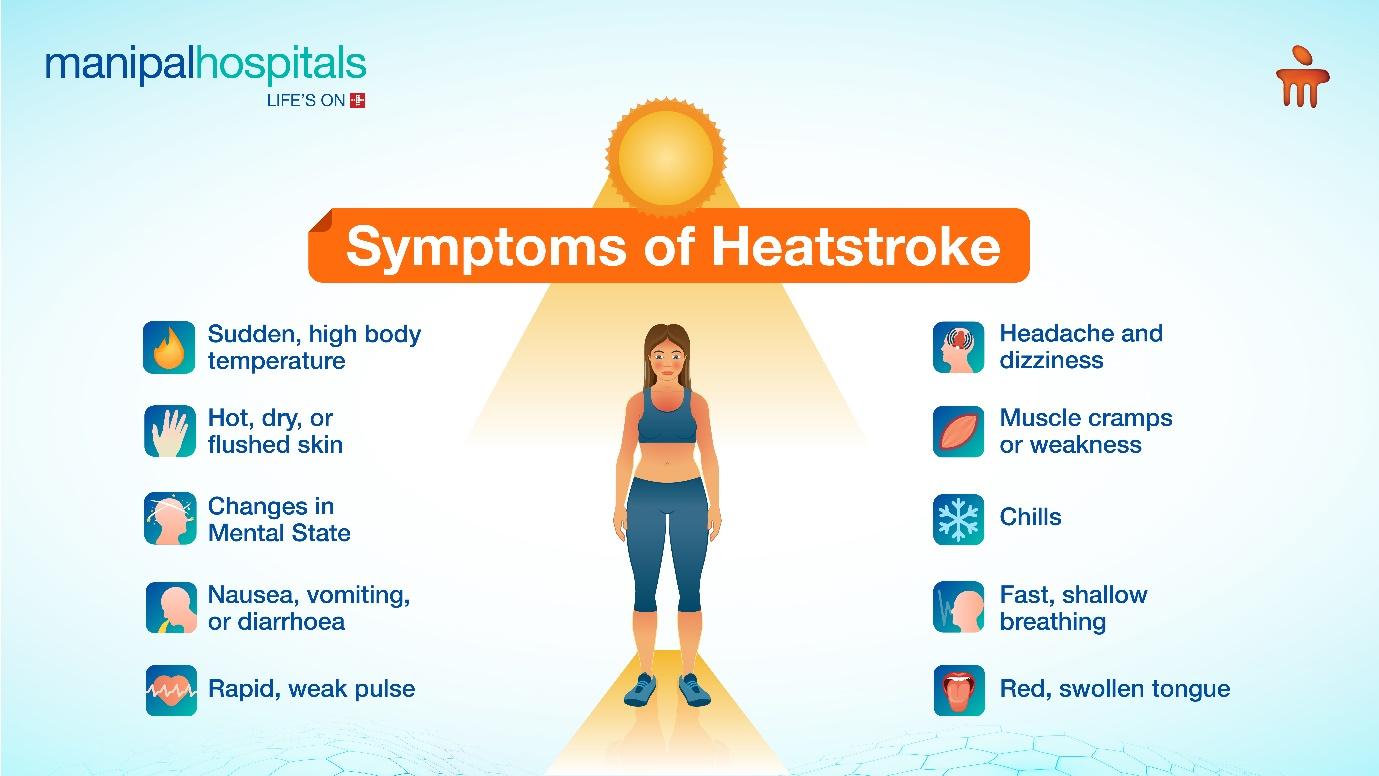
Symptoms of Heatstroke
-
Sudden, High Body Temperature: Core body temperature above 104°F (40°C) is a red alert and hallmark symptom of heatstroke.
-
Hot, dry, or Flushed Skin: Sweating may initially stop, leaving skin unnaturally hot and dry which contributes to the heatstroke.
-
Mental State: Confusion, delirium, or loss of consciousness with other altered mental changes are alarming symptoms.
-
Nausea, Vomiting, or Diarrhoea: The body attempts to expel excess heat, causing digestive upset.
-
Rapid, Weak Pulse: Increased heart rate tries to compensate for circulatory issues as the body attempts to cool itself down.
-
Headache and Dizziness: Impaired blood flow affects the brain, causing these symptoms.
-
Muscle Cramps or Weakness: Overheated muscles may experience cramping or fatigue. Mostly, it occurs due to Electrolyte imbalances and dehydration.
-
Chills: Paradoxical chills can sometimes occur despite the high core temperature.
-
Fast, Shallow Breathing: Respiratory distress may occur as the body's ability to regulate breathing is compromised.
-
Red, Swollen Tongue: Dehydration and impaired circulation can cause these symptoms of a sun stroke.
When to Seek Help
If you suspect heatstroke, immediate action is critical:
-
Call Emergency Services: This is crucial for prompt medical attention.
-
Move the Person to a Cool, Shaded Area: Remove excess clothing and fan them gently.
-
Apply Cool, Wet Cloths to their Skin: Do not use ice directly.
-
Offer cool water or Electrolyte Drinks: If conscious, sip fluids gradually.
-
Monitor Vital Signs: Check temperature, pulse, and breathing until help arrives.
Heatstroke is a severe medical emergency that requires prompt recognition and treatment. It is important to understand its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures to effectively mitigate its risks and safeguard our health during hot weather conditions. Stay vigilant, stay hydrated, and prioritise your well-being to prevent the adverse effects of heatstroke and enjoy the summer safely. Please consult our expert Neurologist at Manipal Hospitals, Saltlake, for further assistance with heatstroke.
FAQ's
Yes, heatstroke can happen indoors, especially in poorly ventilated, hot environments.
Untreated heatstroke can lead to organ damage, brain complications, and even death.
You can prevent heatstroke by staying hydrated, avoiding strenuous activity during peak heat hours, wearing loose, breathable clothing, using sunscreen, and taking cool breaks often.
Yes, certain chronic illnesses like heart disease, obesity, and kidney disease can increase susceptibility to heatstroke. Discuss preventive measures with your healthcare provider if you have any underlying conditions.
Untreated or severe heatstroke can lead to brain damage, organ dysfunction, and long-term complications. Prompt medical response and early intervention are vital.





















 3 Min Read
3 Min Read