
Sunburns are a common summertime woe but are more than just a temporary inconvenience. This painful reddening of the skin is caused by overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun and can have lasting consequences for your skin's health. Let's delve deeper into understanding sunburns, their causes, symptoms, and how to soothe the burn while minimising long-term risks.
Synopsis
What is Sunburn?
Sunburn is a skin condition when the outer layer of the skin gets tanned with a painful inflammatory reaction caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation. These rays come in three forms, such as UVA (Ultraviolet A), UVB (Ultraviolet B), and UVC (Ultraviolet C). UVA rays penetrate the deepest, contributing to premature ageing and wrinkles. UVB rays are the primary culprit behind sunburns, damaging skin cells and triggering inflammation. Though, the atmosphere absorbs most UVC rays before they reach the Earth's surface.
Sunburns aren't just a cosmetic concern. They represent an inflammatory response by the body, a sign that your skin's defences have been overwhelmed. Repeated sunburns can weaken the skin's barrier function, making it more susceptible to infection and dehydration. Furthermore, sunburns significantly increase the risk of developing skin cancer later in life.
Types of Sunburn?
There are three types of sunburns based on the severity of the skin damage. Such as:
-
First-degree: In this, the outer layer of the skin gets damaged and heals on its own with time.
-
Second-degree: Damages the middle sections of the skin with blisters and painful inflammation. This may take a few weeks to heal and even sometimes require medical intervention.
-
Third-degree: This is a very rare type of sunburn and needs emergency treatment. In this, all the layers of the skin get damaged, including the fat layers and nerves.
What are the Stages of Sunburn?
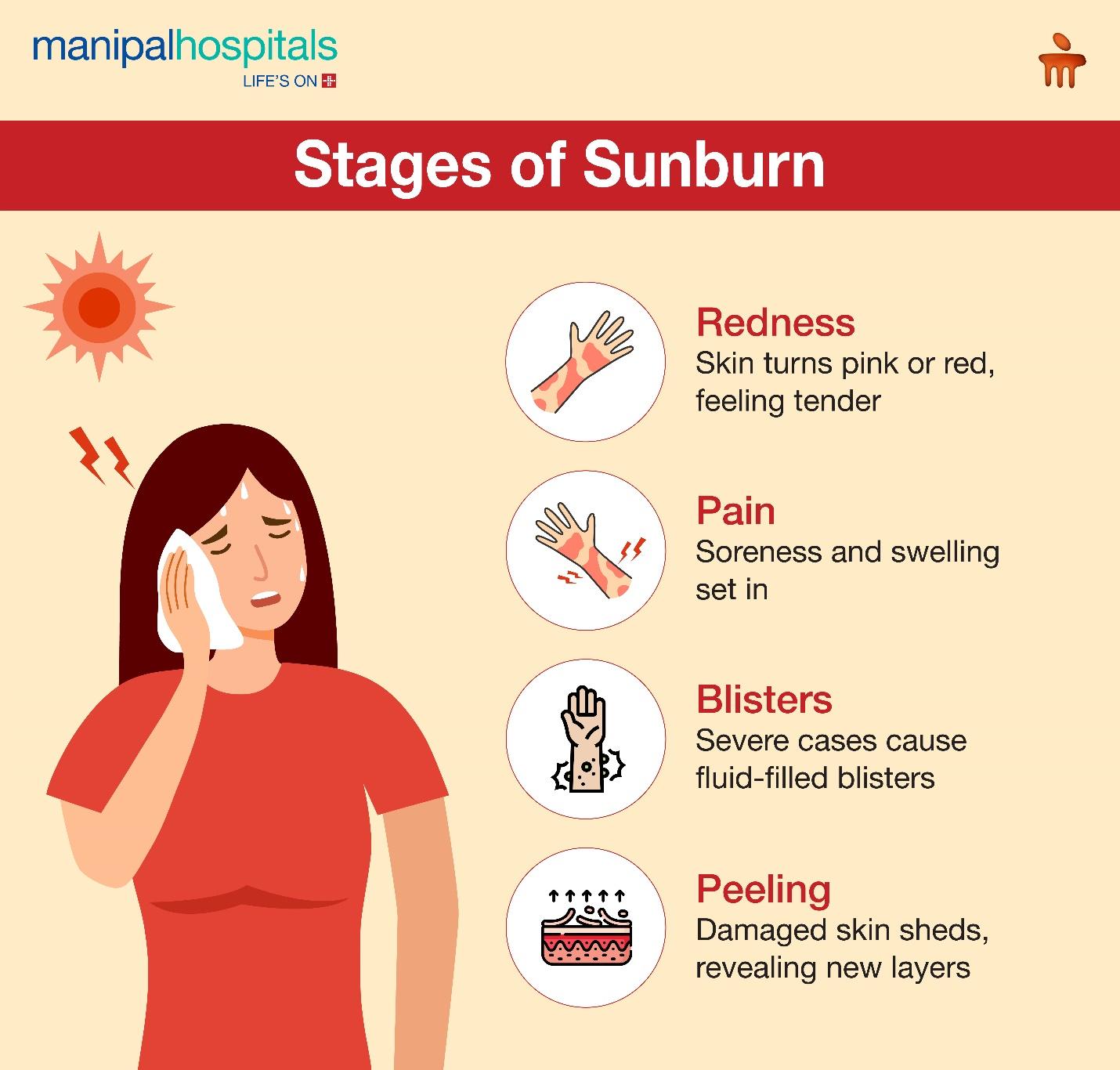
Sunburn symptoms typically develop within a few hours of sun exposure, though the full impact may not be evident for 24-48 hours. Here's a breakdown of the sunburn timeline:
-
Redness and tenderness: The initial sign is often a pinkish or reddish hue to the sun-exposed skin. You may feel tenderness in the affected area.
-
Pain and inflammation: As the sunburn progresses, the skin becomes increasingly sore and painful. Inflammation can cause swelling, especially around blisters.
-
Blistering: In more severe cases, blisters filled with clear fluid may form on the sunburnt skin. These blisters can be itchy and uncomfortable.
-
Peeling: After a few days, the damaged outer layers of skin begin to peel, revealing new skin cells underneath. This peeling may be patchy or sheet-like.
While these symptoms are unpleasant, they usually resolve within a week or two with proper care. However, if you experience chills, fever, severe pain, or extensive blistering, consult a dermatologist immediately.
Effect of Sunburn
The shadow of sunburn goes beyond the initial discomfort. Here are some long-term risks to be aware of:
-
Premature skin ageing, such as wrinkles, fine lines, and loss of skin elasticity.
-
Increased risk of skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest form.
-
Skin sensitivity to UV rays increases the likelihood of future burns.
What are the Treatment Options for Sunburn?
The first- and second-degree sunburns can be treated at home with proper care. Here are some treatment options to alleviate the discomfort and promote healing:
-
Cool compress: Apply cool compresses or take a cool bath to soothe the burning sensation. Avoid hot showers or baths, as they can further irritate the skin.
-
Moisturise your skin well: Use a gentle, fragrance-free moisturiser to replenish lost moisture and prevent the skin from drying out. Aloe vera gel is a natural option known for its soothing properties.
-
Use pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation.
-
Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated, as sunburn can lead to dehydration.
Home Remedies for Sunburn Relief
Here are some additional home remedies often recommended for sunburn relief:
-
Oatmeal bath: Colloidal oatmeal baths can help reduce inflammation and itching.
-
Apple cider vinegar: Diluted apple cider vinegar applied with a cool compress may provide some relief, although research is limited.
-
Yoghurt: Applying plain, cool yoghurt to the sunburn can offer a soothing effect.
These are home remedies, and their effectiveness can vary. If your sunburn is severe or doesn't improve with home care, consult a doctor.
Note: Avoid picking at or popping blisters, as this can increase the risk of infection.
Conclusion
Sunburns are a preventable condition. If we take some measurements while going out during peak hours by carrying an umbrella, cap, and hat with wide brims; wearing long-sleeved clothes; and wearing sunglasses to block UVA and UVB. By following these sun safety tips, you can enjoy the outdoors without putting your skin's health at risk. In case of sunburn or any skin-related issue, you may also contact Manipal Hospitals, Salt Lake.
FAQ's
While sunburns and sun allergies (sun poisoning) can share some symptoms like redness and pain, there are key differences. Sunburns typically affect all sun-exposed areas, while sun allergies may cause a patchy rash with bumps or hives.
Most sunburns heal within a week or two with proper care. However, the severity of the sunburn impacts healing time.
Sunburnt skin naturally peels as part of its healing process. While you can't completely prevent it, gentle exfoliation and consistent moisturising can help minimise peeling and promote even healing.
While there's no magic bullet for sunburn healing through food, staying hydrated and consuming foods rich in antioxidants like vitamins C and E may aid the healing process. However, a balanced diet and proper topical care remain the foundation for sunburn recovery.
Blisters are a sign of a more severe sunburn. Resist the urge to pop them! Popping blisters increases the risk of infection. Let them heal naturally and keep the area clean. If blisters are large or painful, consult a doctor.
Yes, sunscreen is still important even on sunburnt skin. It helps prevent further sun damage as the burnt skin heals and is more sensitive. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher.
Repeated sunburns can cause premature ageing, increased skin sensitivity, and heightened risk of skin cancer, including melanoma.
Sunburn is caused by UV radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. UVB rays are the main culprits behind sunburn, while UVA rays contribute to skin ageing.
The best sunburn treatment at home includes applying aloe vera gel, taking cool baths, staying hydrated, and using fragrance-free moisturisers to soothe and heal the skin.
To treat sunburn on the face quickly, apply aloe vera gel or a soothing, fragrance-free moisturiser. Take cool baths or apply cool compresses to reduce heat and inflammation.





















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read















