-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
- Access Lab Reports
-
-
Book Appointments & Health Checkup Packages
-
Centre of
Excellence
Centre of Excellence
- Bariatric Surgery - MIBS
- Accident and Emergency Care
- Cancer Care
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Vascular Surgery
- Gastrointestinal Science
- General Surgery and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Hemato Oncology
- Institute of Orthopaedics and Sports Medicine
- Liver Transplantation Surgery
- Neonatology & NICU
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatric And Child Care
- Plastic, Reconstructive And Cosmetic Surgery
- Renal Sciences
- Spine Care
- Urology
- Vascular and Endovascular Surgery
Other Specialities
- Anesthesiology
- Bariatric Surgery
- Dental Medicine and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Ear Nose Throat
- General Medicine
- ICU and Critical Care
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Medical Gastro
- Medical Oncology
- Nutrition And Dietetics
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Paediatric Gastroenterology
- Paediatric General Surgery
- Paediatric Urology
- Pain Medicine
- Physiotherapy
- Psychiatry
- Psychology
- Pulmonology (Respiratory and Sleep Medicine)
- Rheumatology
- Robotic Assisted Surgery
- Stroke Care
- Surgical Gastro
- Surgical Oncology
- Trauma Care
- Doctors
- Sarjapur Road
- International Patients



Clinics








- Self Registration
- In-Patient Deposit
- Mars - Ambulance
- Home Care
- Organ Donation
- Academic and Research
- Corporate & PSU
- Insurance Helpdesk
- Awards And Achievements
- Manipal Insider
- Careers
- Contact Us

Viral fever and food infections
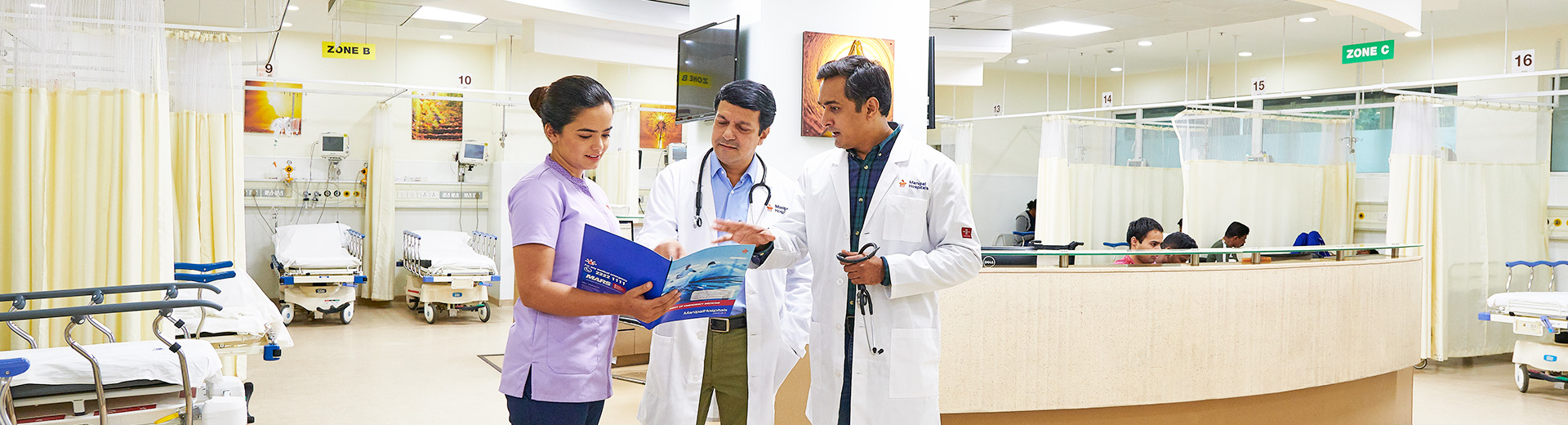
General medicine hospital in Bangalore
Viral fever and food infections are both illnesses that can be caused by consuming contaminated food or water. Viral fever is caused by a virus, while food infection is caused by bacteria, parasites, or other pathogens. Symptoms of viral fever include fever, chills, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches. Symptoms of food infection include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and abdominal pain. Both illnesses can be serious, and both require prompt medical treatment.
Viral fever is caused by a virus, a tiny infectious particle that replicates inside the cells of its host. There are many different types of viruses that can cause a wide range of diseases. The virus that causes viral fever spreads through contact with contaminated bodily fluids, such as blood, saliva, or mucus. It can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as doorknobs, door handles, or countertops.
Once the virus enters the body, it begins replicating inside the cells, which can cause the cells to become damaged and die. As the virus replicates, it causes the body to produce antibodies to fight it off. The production of antibodies causes viral fever symptoms, such as fever, chills, and fatigue.
Symptoms of viral fever
Some common symptoms of viral fever are:
-
High-grade fever
-
Headache (mild to severe)
-
Sore throat
-
Runny nose or nasal congestion
-
Muscle pain and joint pain
-
Diarrhoea or/and abdominal pain
-
Nausea / Vomiting
-
Fatigue
-
Dizziness
-
Chills
-
Redness or burning of eyes
-
Rashes on skin
-
Loss of appetite
Causes of viral fever
Viral fever can be caused due to various reasons. Some of the causes of viral fever are:
-
Inhaling virus-containing droplets from an infected person can also transmit viral fever. The most common cause of viral fever is seasonal flu.
-
Sharing food or drinks with a virally infected person can also result in viral fever transmission.
-
Contaminated water is another source of viral fever, particularly in children.
-
Viral fever can also be transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person's bodily fluids.
-
Insect (mosquitoes and ticks) and rodent (mice) bites can transmit the virus that causes viral fever to humans.
-
Blood exchange with an infected person during drug abuse can also result in viral fever.
Treatment for viral fever
The treatment for viral fever is determined by the type of viral infection and the severity of the symptoms. For low-grade viral fever, doctors usually try to prescribe paracetamol or ibuprofen. Warm baths and electrolyte solutions can also help with muscle aches, fatigue, and diarrhoea. Book an appointment to have the best treatment.
To relieve the discomfort of high-grade fever, your doctor may prescribe a high dose of paracetamol to be taken more frequently (every 4-6 hours). The prescribed treatments should not be stopped without first consulting your doctor. For critically ill patients, paracetamol can be injected intravenously to lower the temperature and bring it closer to normal.
The doctor may also prescribe antibiotics to prevent secondary bacterial infections, which should be taken at the prescribed dose, frequency, and duration.
Symptoms of food infections
Some common symptoms of food infections are:
-
Nausea
-
Vomiting
-
Watery or bloody diarrhoea
-
Abdominal pain and cramps
-
Fever
Treatment for food infections
Treatment for food infections is typically determined by the source of the illness if known, and the severity of your symptoms. Most people recover without treatment after a few days, though some types of food poisoning can last longer. Visit our general medicine hospital in Bangalore for the best treatment
Some treatments include:
Replacement of fluids lost - Fluids and electrolytes — minerals such as sodium, potassium, and calcium that keep the fluid balance in your body — that are lost due to persistent diarrhoea must be replaced. Some children and adults with persistent diarrhoea or vomiting may require hospitalisation so that salts and fluids can be administered through a vein (intravenously) to prevent or treat dehydration.
Antibiotics - If you have a specific type of bacterial food poisoning and your symptoms are severe, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Listeria food poisoning requires hospitalisation and treatment with intravenous antibiotics. The sooner you start treatment, the better. Prompt antibiotic treatment during pregnancy may help keep the infection from affecting the baby.
Antibiotics will not help with viral food poisoning. In some cases of viral or bacterial food poisoning, antibiotics may aggravate symptoms. Discuss your options with your doctor.
Home Sarjapurroad Specialities General-medicine Viral-fever-and-food-infections

You’re on Our Indian Website
Visit the Global site for International patient services










