Types of Irregular Heartbeat
An irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia, happens when the heart doesn’t beat in a steady rhythm. It can be too fast, too slow, or feel like it skips a beat.
Here are the main types of irregular heartbeats explained in simple terms:
1. Fast Heartbeat (Tachycardia)
This is when your heart beats faster than normal, often over 100 beats per minute.
-
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): The heart’s upper chambers (atria) beat out of sync with the lower chambers, causing a fluttering or irregular pulse.
-
Atrial Flutter: Similar to AFib but with a more regular rhythm.
-
Ventricular Tachycardia: A dangerously fast rhythm in the lower chambers of the heart, which can lead to serious problems.
-
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): A very fast heartbeat starting in the upper part of the heart.
2. Slow Heartbeat (Bradycardia)
This is when the heart beats slower than 60 beats per minute.
-
It might be normal for some people, like athletes, but it can mean the heart’s electrical system isn’t working well in others.
-
Heart Block: A condition where the signals telling the heart to beat move too slowly, causing the heart to pump less blood.
3. Skipped or Extra Beats (Premature Beats)
Sometimes, the heart feels like it skips a beat or beats extra. These are usually harmless and happen in healthy people too.
4. Serious Irregular Rhythms (Ventricular Fibrillation)
This is when the lower part of the heart shakes instead of pumping blood. It’s a life-threatening condition that needs emergency treatment right away.
What are the Causes of Irregular Heartbeat?
An irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia can be triggered by various factors. Some causes are temporary and harmless, while others might indicate a more serious heart condition. Here are the common reasons for an irregular heart rhythm:
1. Heart Conditions
-
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Blocked or narrowed blood vessels that supply the heart can lead to irregular heartbeats.
-
Heart Attack: Damage to the heart muscle can interfere with the electrical signals that control the heartbeat.
-
Heart Valve Problems: Issues with heart valves can cause improper blood flow, leading to an irregular rhythm.
-
Heart Failure: When the heart is weak and unable to pump blood efficiently, it can trigger arrhythmias.
2. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
When blood pressure is high, it puts extra strain on the heart, which can lead to irregular rhythms over time.
3. Electrolyte Imbalance
Minerals like potassium, sodium, and calcium are essential for the heart’s electrical signals. If these minerals are out of balance, it can cause irregular heartbeats.
4. Overactive or Underactive Thyroid
The thyroid regulates metabolism. If it’s too active (hyperthyroidism) or not active enough (hypothyroidism), it can affect the heart’s rhythm.
5. Stress or Anxiety
High stress or anxiety can cause temporary irregular heartbeats. Stress hormones can speed up the heart or make it feel irregular.
6. Stimulants
Caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, and certain drugs can stimulate the heart, leading to irregular beats. Overuse of these substances can increase the risk of arrhythmias.
7. Sleep Apnea
This condition, where breathing stops and starts while you sleep, can cause the heart to beat irregularly, especially in people with untreated sleep apnea.
8. Age
As people get older, the heart’s electrical system may change, making arrhythmias more likely.
9. Genetics
Some people are born with heart conditions or an inherited risk for arrhythmias. If family members have had arrhythmias, it’s important to monitor your heart health.
What are the Treatments for Irregular Heartbeat?
If you have an irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia, there are several treatment options available to help restore a normal rhythm and reduce the risk of complications. The treatment your doctor recommends will depend on the type and cause of the arrhythmia. Here’s an overview of common treatments in simple terms:
1. Medications
-
Anti-arrhythmic Drugs: These medicines help control the heart’s rhythm and bring it back to normal.
-
Blood Thinners: If you have arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation, you might need blood thinners to prevent blood clots, which could lead to a stroke.
-
Beta-blockers or Calcium Channel Blockers: These drugs slow the heart rate and reduce the chances of abnormal rhythms.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Sometimes, simple changes to your daily routine can help manage irregular heartbeats:
-
Reduce Stress: Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can calm your heart.
-
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Cutting back on stimulants can help prevent irregular heart rhythms.
-
Healthy Diet and Exercise: Eating well and staying active can improve heart health and reduce the risk of arrhythmias.
3. Electrical Cardioversion
This is a procedure where doctors use electric shocks to reset the heart’s rhythm back to normal. It’s often used for arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
4. Catheter Ablation
If medications and electrical shocks don’t work, a procedure called catheter ablation might be recommended. Doctors thread a thin tube (catheter) through a blood vessel to your heart and use it to destroy the tissue causing the irregular rhythm. This can help the heart return to a normal pace.
5. Pacemaker
A pacemaker is a small device that’s implanted under the skin of your chest. It sends electrical signals to help the heart beat at a normal rate, especially in cases of slow heartbeats (bradycardia).
6. Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD)
For those with life-threatening arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation, an ICD might be recommended. This device monitors the heart's rhythm and delivers shocks if it detects a dangerously irregular heartbeat, preventing a heart attack or cardiac arrest.
7. Surgery
In rare cases, surgery might be needed to correct severe arrhythmias, such as repairing heart valves or fixing abnormal heart structures that are causing the irregular rhythm.
8. Monitor and Follow-Up
Even with treatment, regular check-ups with your doctor are important to keep an eye on your heart’s health and adjust treatments if necessary.
7 Simple Tips to Keep Your Heartbeat Healthy and Strong
Maintaining a healthy heartbeat is key to overall well-being. Here are 7 simple tips to keep your heart rhythm steady and prevent irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia):
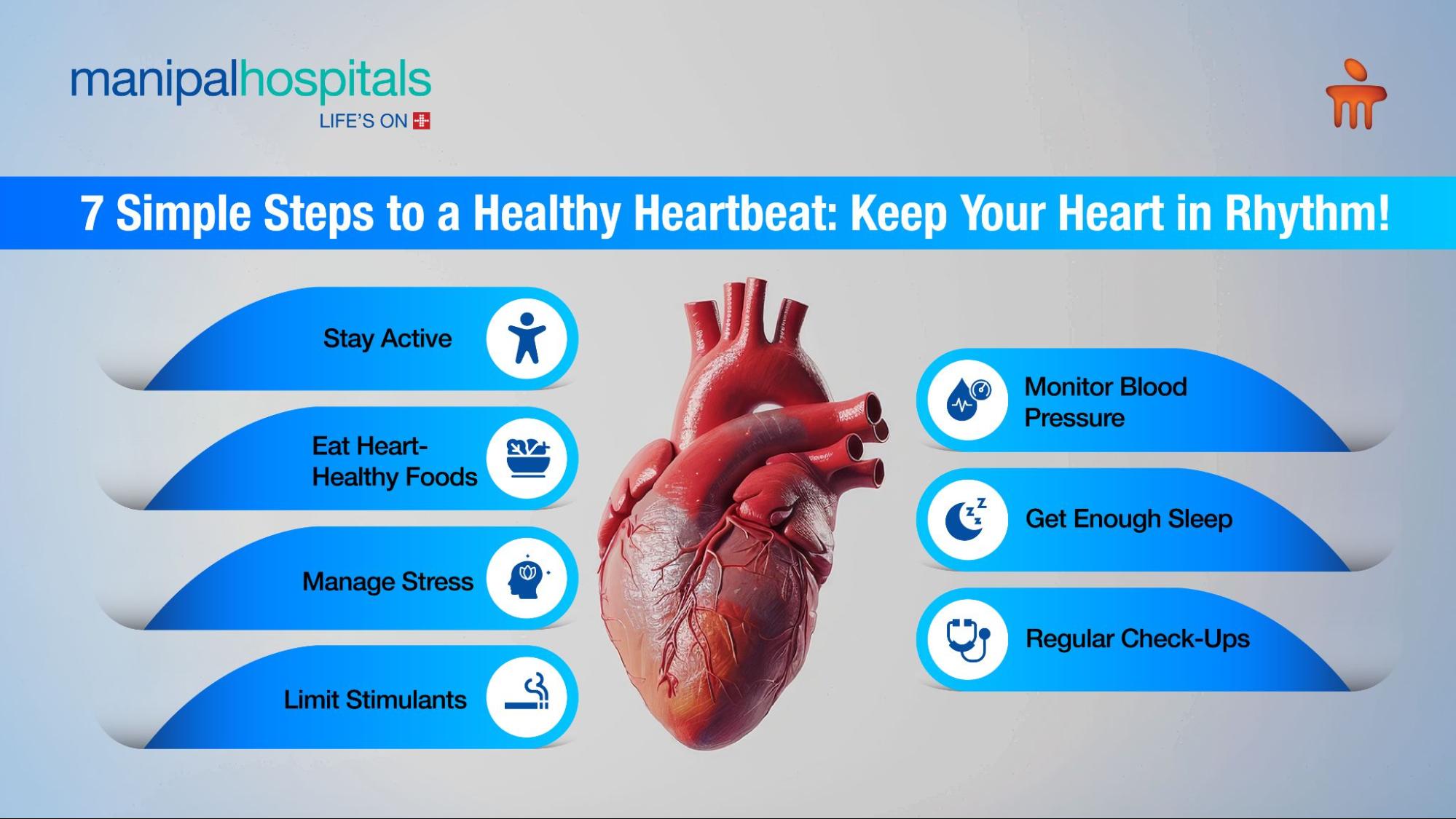
-
Stay Active – Regular exercise strengthens your heart, improves blood flow, and reduces the risk of cardiac arrhythmia.
-
Eat Heart-Healthy Foods – A balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps lower cholesterol and blood pressure, supporting a healthy heart arrhythmia.
-
Manage Stress – Reducing stress through relaxation techniques can prevent abnormal heart rhythms caused by anxiety.
-
Limit Stimulants – Cutting back on caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol helps maintain a steady heart rhythm.
-
Monitor Blood Pressure – Keep your blood pressure in check to avoid unnecessary strain on your heart and reduce the risk of arrhythmias.
-
Get Enough Sleep – Adequate rest supports heart health and helps prevent irregular heartbeats.
-
Regular Check-Ups – Regular visits to the doctor ensure early detection of irregular heartbeat symptoms and help keep your heart in top shape.
When to consult a doctor for an irregular heartbeat?
If you experience any unusual irregular heartbeat symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice. While occasional palpitations may not be a cause for concern, certain signs and symptoms require professional evaluation to ensure your heart is healthy. Here’s when you should consult a doctor:
1. Frequent or Persistent Palpitations
If you often feel your heart pounding, fluttering, or skipping beats, it could be a sign of arrhythmia. While occasional palpitations can be harmless, frequent or persistent symptoms should be checked by a doctor.
2. Dizziness or Lightheadedness
An irregular heartbeat can cause dizziness or a feeling of faintness. If this happens regularly or suddenly, it could indicate that your heart isn’t pumping blood efficiently, and medical attention is needed.
3. Shortness of Breath
Difficulty breathing or feeling winded, especially when doing routine activities, may be linked to an underlying heart condition, including heart arrhythmia.
4. Chest Pain or Discomfort
Chest pain, tightness, or discomfort alongside an irregular heartbeat could be a sign of a more serious problem, such as a heart attack or severe arrhythmia. Immediate consultation with a doctor is crucial.
5. Fainting or Near-Fainting Episodes
If you faint or feel like you’re about to faint, this could be a sign of a dangerous abnormal heart rhythm. Seek medical help right away.
6. Family History of Heart Disease or Arrhythmia
If you have a family history of cardiac arrhythmia or heart disease, it’s essential to get regular check-ups, even if you don’t currently have symptoms. You may be at a higher risk for developing arrhythmias.
7. Increased Fatigue
Unexplained tiredness, especially when it’s out of proportion to your usual activity level, can be related to an underlying heart condition, including irregular heartbeats.
Don’t ignore these signs, and consult your healthcare provider as soon as possible. Early detection of irregular heartbeat symptoms can lead to better treatment outcomes and a healthier heart.





























