
Listen to article
Loading audio...
]Eardrum damage, also known as ruptured eardrum, is a hole or tear within the eardrum that affects the hearing and sense of balance in individuals. Most often, damaged eardrums heal on their own. But sometimes, individuals may require surgery to fix their damaged eardrum.
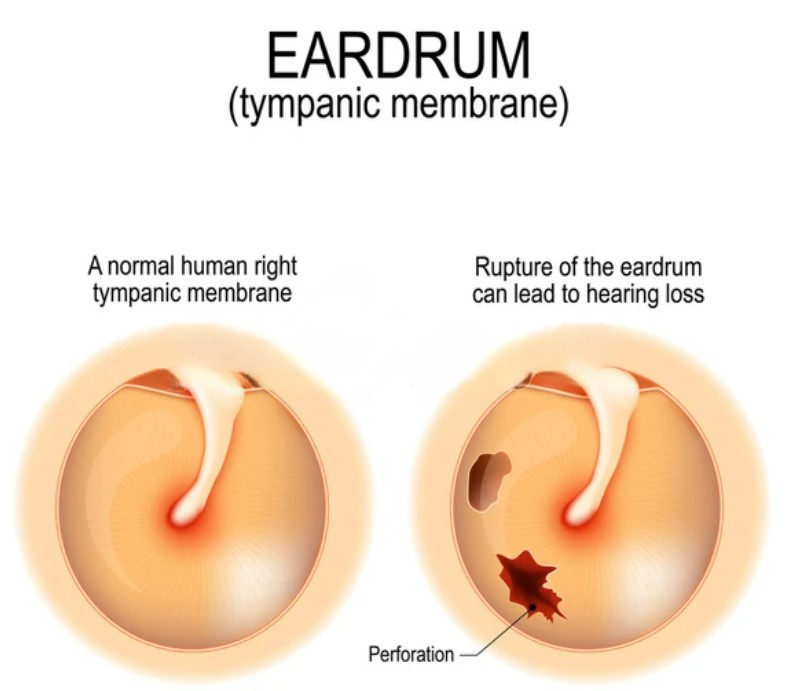
What is Eardrum Damage?
The inner ear and outer ear are separated by a flexible membrane called the tympanic membrane or the eardrums, which is a thin tissue. When sound waves enter your ear, this membrane vibrates. The vibration travels through the middle ear bones. As this vibration allows the individual to hear, if their eardrum is broken, their hearing may suffer. If someone has a serious middle ear infection or if they harm or injure their eardrum, it may explode. Hence, hearing and the feeling of balance may be impacted by a damaged eardrum. Eardrum damage is frequently recovered on its own. However, to fix the damaged eardrum, surgery may be recommended. The best defence against eardrum rupture is protection.
Causes of Eardrum Damage
An ear infection may result in a damaged eardrum. The infection causes pus or fluid to accumulate behind the eardrum. The eardrum may be damaged as the pressure increases. Many other factors are responsible for the eardrum damage, including:
-
Using Cotton Swabs
Any object inserted into the ears increases the risk of infection or injury to the ear canal or eardrum. Cotton swabs are useful for grooming, but they should not be used to clean or remove earwax.
-
Pressure Changes (Barotraumas)
The air pressure in the middle ear and the atmospheric pressure are typically equal. However, activities like scuba diving, travelling in an aeroplane, and driving on a mountain road might result in an abrupt change in pressure that can rupture the eardrum.
-
Loud Noises (Acoustic Trauma)
Sound waves from very loud noises, like an explosion, can damage the eardrum. The cochlea may suffer temporary or permanent loss as a result of loud noise.
-
Head Trauma
The eardrum can be torn open by a direct hit to the head or a serious head injury from something like a vehicle accident.
-
Direct Trauma to the Pinna and Outer Ear Canal
The eardrum can be torn by pressure from objects that put pressure on the ear, such as an open palm slap.
Symptoms of Eardrum Damage
Individuals may not realise they have a damaged eardrum until they notice symptoms such as changes in their hearing or blood and pus oozing from their ears. Typical eardrum damage symptoms include:
- Mild to severe discomfort that may worsen for a time before abruptly decreasing ear discharge that may be clear, pus-filled, or crimson
- Hearing impairment
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears)
- Vertigo (the sensation that the room is spinning)
- Sometimes, weak facial muscles.
Management and Treatment for Eardrum Damage
A fluid sample, an otoscope exam, an audiology exam, and tympanometry are some of the diagnostic approaches that can help identify a damaged eardrum. Patching with a medicated paper patch, antibiotics for infection, or surgery (tympanoplasty) are recommended by the healthcare professional to repair the eardrum. Also, applying warm compresses, avoiding nose blowing, and not using over-the-counter eardrops without the recommendation of one of the top Ent specialists in Vijayawada, are suggested for patients with damaged eardrums.
Prevention of Eardrum Damage
Eardrum damage can be greatly avoided by protecting the ears. Individuals may safeguard their eardrums and ears by following some preventive measures, which are discussed below:
- Keeping the ears dry will help avoid any further infections.
- A gentle stuffing of cotton in your ears is recommended to keep water out of the ear canal while taking a bath.
- One should immediately seek medical attention in the case of any ear infection.
- Middle ear infections should be treated immediately to prevent potential eardrum damage. Hearing loss, nasal congestion, earaches, and fevers are all indications of a middle ear infection.
- One should avoid travelling on aeroplanes when they have a cold or sinus infection.
- The use of earplugs, gum, or a forced yawn is recommended to maintain stable ear pressure.
- One should avoid using foreign objects to remove excess earwax; a daily shower is typically sufficient to maintain a healthy balance.
- Using earplugs is recommended when individuals are aware of their surroundings, which may involve loud machinery, during concerts, on construction sites, or when the noise level is expected to be high.



















 3 Min Read
3 Min Read






.png)





