
Neurological diseases are medical conditions affecting the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and other nerves. The abnormal changes in the functioning and structure within any part of the nervous system may result in a neurological disorder. Altered electrical impulses can occur anywhere in the brain and/or produce various symptoms that are involved in pathologic processes.
Changes in the gene structure or mutations can lead to genetic brain disorders. Hence, these mutations affect the development and function of the brain. Certain hereditary brain disorders result from gene mutations brought on by environmental exposure, such as cigarette smoke. Some diseases are inherited, which implies that a mutated gene or set of genes is passed down through a family. They might also result from a confluence of genetic modifications and environmental influences.
According the neurologists in Vijayawada, the role of genetic components in neurological diseases ranges from direct predisposition such as Huntington's disease and spinocerebellar atrophy to more complex roles such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and prion disorders. Although genetic risk factors have a significant impact on these chronic illnesses, most neuronal diseases are multifactorial in nature, meaning they are influenced by a combination of genes and environment.
How Genetics is Associated with Neurological Disorders?
Neurological problems emerge mostly as a result of genetic causes. The severity and course of neurological illnesses can all be affected by a person's genetic composition, as well as their vulnerability to developing them. Mutations in particular genes are the root cause of some neurological illnesses, including Huntington's disease and familial Alzheimer's disease. In some situations, a person's risk of getting a neurological condition may be increased by genetic variants, but additional environmental factors may also be at play.
The majority of neurological illnesses brought on by gene alterations normally appear in childhood, though they can occasionally occur as early as birth. But other brain conditions brought on by gene mutations don't show themselves until much later in life. It's possible that any symptoms won't become visible until well into adulthood.
Some of the examples involving genetic components include:
-
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
It is known to be the sixth leading cause of death in Western countries. The common symptoms include the prior onset of memory loss followed by cognitive dysfunction and slow progressive dementia over the course of several years. It mostly occurs at the age of 65 and above. However, only 10% of these instances have a clear genetic inheritance pattern called familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD). With a 50% chance of dementia, people with a family history of FAD typically acquire this rare form of Alzheimer's disease between the ages of 30 and 60. Families with early-onset AD have been found to have mutations in three loci, namely presenilin-1 (PSEN1), presenilin-2 (PSEN2), and amyloid precursor protein (APP). Apolipoprotein E (APOE), a gene with frequent variations, significantly increases the risk of Alzheimer's disease in populations all over the globe.
-
Huntington’s Disease (HD)
This condition results in cognitive impairment, psychological and psychiatric changes, involuntary movements, and impaired motor skills. Individuals with a higher risk of Huntington’s disease usually go through genetic counseling, psychological counseling, and a neurological exam before genetic testing is an option.
-
Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
It is characterised by slowness of movement, tremors, rigidity, and gait instability due to the dopamine neurotransmitter's depletion. Numerous genes have been linked to PD, but its genetics are not as clear-cut as those of certain other diseases. Genetic testing is accessible for some uncommon types of PD, but most genetic testing is still in the research stages.
-
Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL)
A personal and/or family history of migraines, stroke-like episodes before the age of 60, cognitive and behavioural issues, and dementia are all signs of CADASIL, a genetic neurological condition. NOTCH3 is the name of the CADASIL-related gene. Genetic testing is available for people with a personal or family history of CADASIL. Approximately 90% of people with CADASIL will have a detectable genetic change in the NOTCH3 gene.
A neurological illness affects many people for the first time in their family. Genetic testing frequently reveals a gene mutation in a person with a neurological illness that neither occurs in other family members nor was inherited from a parent. In a family, this is referred to as a de novo, or fresh, gene mutation. Neurological illnesses caused by altered genes in other families may be passed down from ancestors. One can learn more about the genetics of the neurological condition in their family by speaking with their doctor or a genetic counsellor.
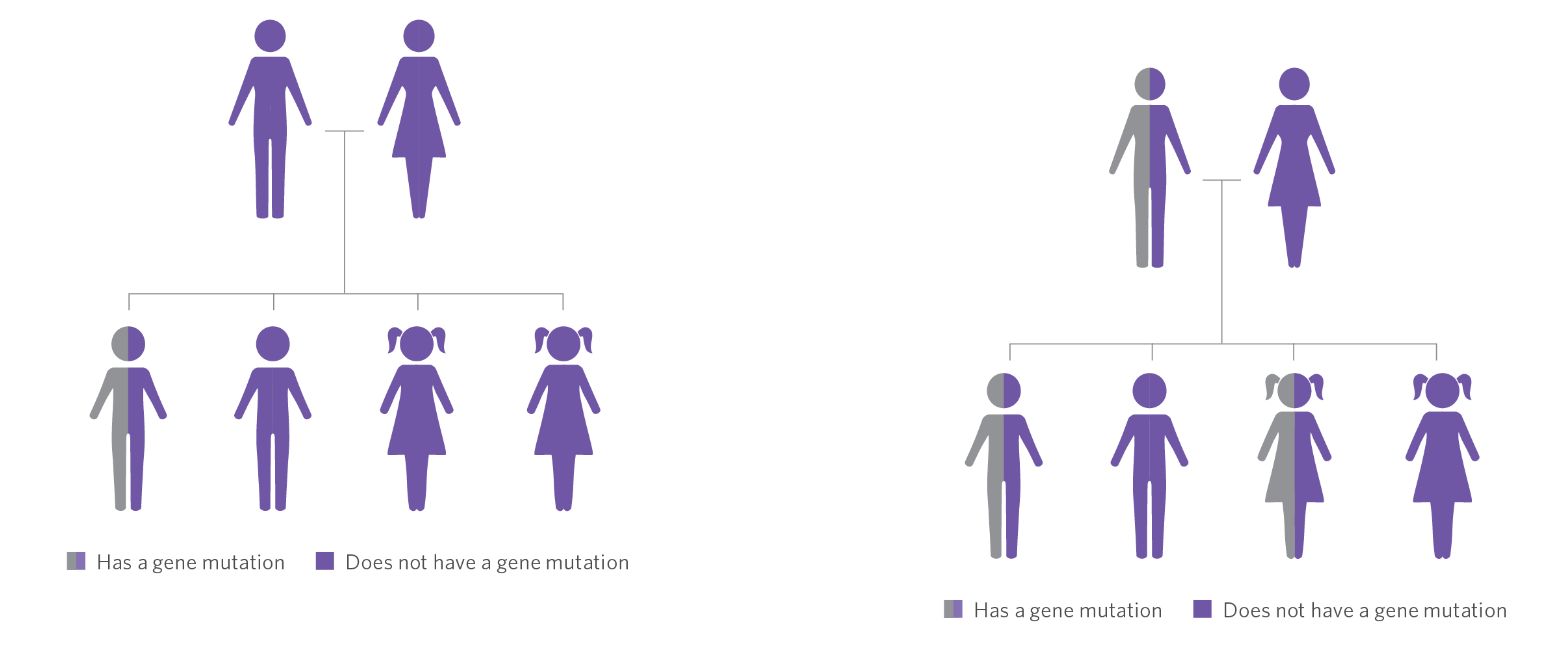
Figure: Chances of neurological diseases running in families
Genetics’ Role in Neurological Disorders?
Neurological conditions can result from gene alterations. A neurological illness might result from a gene alteration that alters how our brain, spinal cord, and other nerves are instructed. Different situations call for the use of genetic testing to determine the origin of the neurological disorders. Depending upon the results of the genetic test, the medical professionals at a top neurology hospital in Vijayawada can inform the individuals more effectively on what to anticipate.
-
Genetic Testing
It is a technique used in laboratories to check for chromosome, gene, or expression alterations in human cells or tissue. These alterations could be symptoms of an illness or condition, including cancer. The most effective method for subtyping neurological illnesses is genetic testing, which also gives the data required to make knowledgeable, individualised therapy and management decisions. Recent technological developments, in particular next-generation DNA sequencing methods, have sped up the identification of the genes responsible for neurological disorders and opened up new avenues for genetic diagnostic testing. A high number of genes can be examined in a single reaction due to the development of techniques for combining targeted capture and massively parallel DNA sequencing. Gene panels and exome sequencing can be used now to do diagnostic genetic testing. This enables a more accurate diagnosis of many neurological illnesses, and genetic testing should now be taken into account early in the diagnostic process.
Frequently asked Questions (FAQs)
Which genetic disorder can lead to a neurological disorder?
The three genetic neurological conditions that are responsible for damaging the complete nervous system include neurofibromatosis, Huntington's disease, and myotonic dystrophy.
What is the most common inherited neurological disorder?
According to the neurologists in Vijayawada, one of the most prevalent inherited neurological disorders is CMT, also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy, which has affected a major population across the globe.
Can neurological problems be genetic?
Despite the fact that the majority of neurological disorders are not hereditary, some diseases, like Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and Alzheimer's disease, may run in families. For these and other hereditary neurological conditions, genetic testing is recommended.
Which neurological condition can be detected by a genetic test?
Genetic testing is recommended for several neurological conditions such as Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD), Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and many more. Accurate genetic testing at a neurology hospital in Viajayawada is essential for diagnosis, making knowledgeable treatment options, and finding additional family members who could be at risk.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read










.png)





