
Blood cancer is a broad term encompassing various malignancies that affect blood and bone marrow, casting a long shadow across the globe. This condition occurs when abnormal blood cells disrupt normal blood function and require prompt diagnosis and treatment. The incidence of blood cancer in India is on the rise necessitating awareness and proactive measures. While its presence can evoke fear and uncertainty, knowledge empowers both the patients and healthcare professionals to combat this complex disease with the required diagnosis approaches and timely interventions.
Synopsis
An Overview: Blood Cancer
Blood cancer arises from the uncontrolled growth of abnormal blood cells, affecting bone marrow, lymphatic system and blood cells that compromise immunity and vital functions. This disrupts the production of healthy red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, leading to a cascade of health issues.
In India, the prevalence of blood cancer is significant, with thousands of new cases diagnosed annually. Despite the challenges, medical institutions like Manipal Hospitals are equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and expertise to address blood cancer effectively, enhancing the chances of recovery and quality of life for patients.
Types of Blood Cancer
Blood cancer encompasses several types, including many subtypes. They are
- Leukaemia- This is the most common cancer among young adults and also children. It usually affects the white blood cells and it can be acute and chronic.
- Lymphoma-This type of cancer originates in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's germ-fighting network.
The lymphatic system includes the lymph nodes (lymph glands), spleen, thymus gland and bone marrow. Lymphoma can affect all those areas as well as other organs throughout the body.
-
Myeloma- Myeloma poses a detrimental impact on plasma cells in the bone marrow, leading to severe bone damage and critical kidney problems.
Each type of cancer presents district characteristics and requires treatment approaches.
Causes of Blood Cancer
Blood cancer stems from mutated DNA in blood cells, causing abnormal growth and crowding out healthy cells. While the exact cause remains unclear, several factors are suspected:
-
Leukaemia: Genetic and environmental triggers, potentially involving chromosomal aberrations, may lead to uncontrolled cell growth.
-
Lymphoma: Gene mutations in lymphocytes cause them to multiply excessively and evade natural cell death. Infections or weakened immunity might play a role. Certain Virus Infections also cause Lymphoma.
-
Myeloma: Plasma cell mutations cause uncontrolled reproduction, with potential links to chromosomal changes affecting growth control genes.
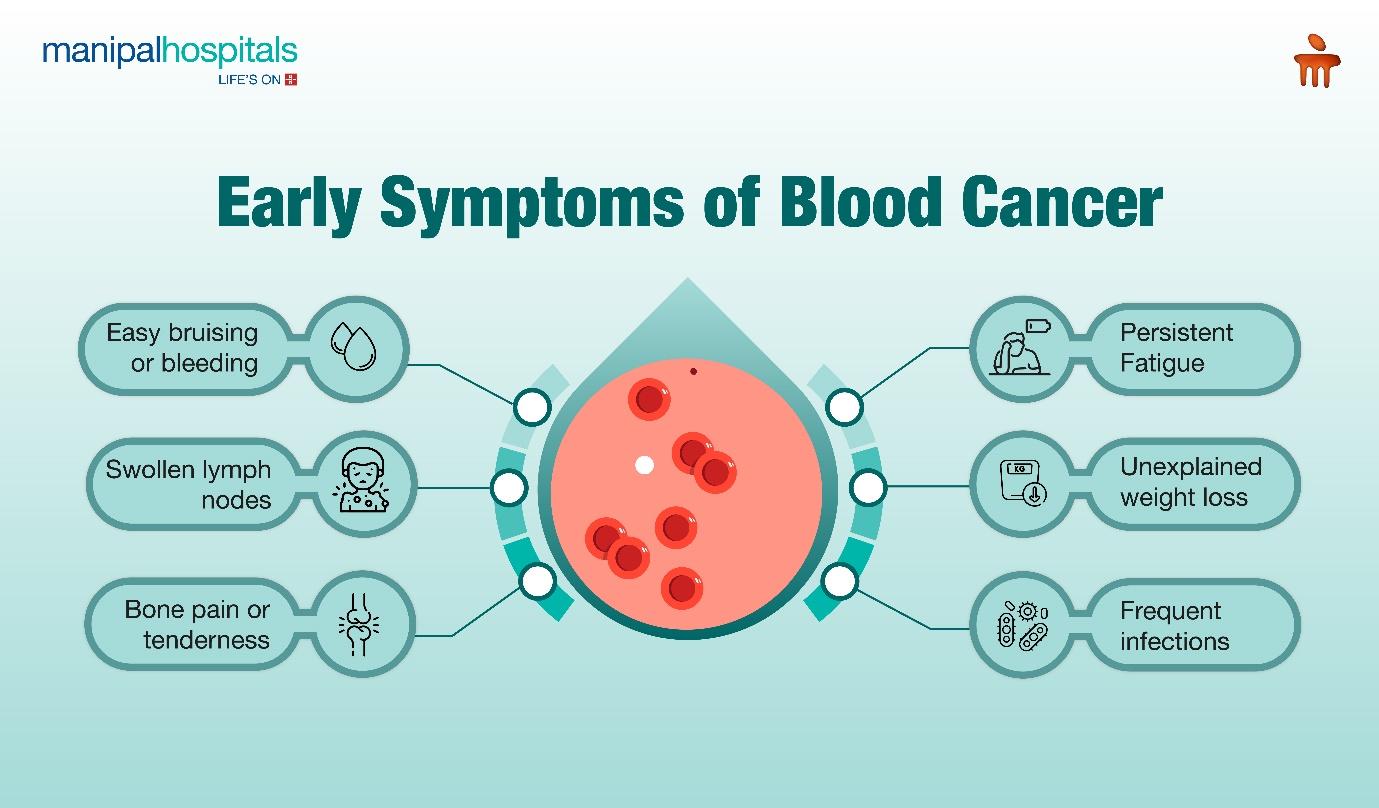
Early Blood Cancer Symptoms may include:
- Persistent fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Bone pain or tenderness
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing blood cancer involves a series of tests and evaluations to confirm the presence of abnormal blood cells and determine the specific type and severity of the disease. Key diagnostic approaches include:
- Blood tests: Assessing blood cell counts and identifying abnormal cells.
- Bone marrow biopsy: Extracting a sample of bone marrow for analysis.
- Flow cytometry
- Imaging studies: Including CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans to assess organ involvement.
- Genetic testing: Identifying specific genetic mutations associated with blood cancer.
Management and Treatments
Treatment for blood cancer depends on the type, stage, and individual patient factors. Common treatment modalities include:
-
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is the first choice, and employs potent medications to eradicate cancer cells within the body.
-
Radiation Therapy: This treatment method focuses intense, high-energy radiation on cancerous cells to impede their growth and division.
-
Stem Cell Transplantation: Stem cell transplantation involves the replacement of damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells, which can regenerate and restore proper blood cell production.
-
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy works by enhancing the body's natural immune response to identify and eliminate cancer cells, empowering the immune system to effectively combat the disease.
The treatment plan may involve a combination of these approaches, tailored to the patient's unique needs and response to therapy. Ongoing monitoring and supportive care are essential to manage side effects and optimise treatment outcomes.
Blood cancer is a complex and challenging condition that requires comprehensive care and management. Early detection through regular screenings and awareness of symptoms is crucial for timely intervention. With advances in medical technology and expertise, institutions like Manipal Hospitals Vijayawada, offer hope and support to patients battling blood cancer. By staying informed and proactive, we can empower individuals and communities to combat this disease effectively.
For expert consultation and personalised care for blood cancer, contact Manipal Hospitals, Vijayawada, today. Our multidisciplinary team of specialists is dedicated to providing compassionate and cutting-edge treatment options to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
FAQ's
Various factors contribute to blood cancer, including age, family history, radiation exposure and certain genetic mutations can increase the risk.
No, blood cancer is not contagious.
The latest advancements include Immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and personalised medicine revolutionising treatment options.
Diagnosis involves blood tests, bone marrow aspiration, biopsy, and imaging studies like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans.
The survival rates vary based on the type and stage of blood cancer. Some types, like acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia, Lymphomas, and Acute promyelocytic leukaemia have higher survival rates.





















 3 Min Read
3 Min Read

















