
Blood cancer is a life-threatening disease. It disrupts the normal production and functioning of blood cells. Blood cancer leads to several health complications, starting from fever and fatigue to abrupt weight loss, joint pain, and so on. However, the symptoms of blood cancer can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease.
Early diagnosis of blood cancer helps in better treatment planning. However, early diagnosis is not always possible because some blood cancers, like lymphoma, are asymptomatic in the early stages. The response to the treatments completely depends on the patient’s age and their health condition. Let’s understand different types of blood cancer in this blog.
What is Blood Cancer?
The malignant transformation of blood-forming cells causes blood cancer. It leads to the uncontrolled growth and division of abnormal cells. These cells interfere with the functioning of normal blood cells. Thus, our body’s power to fight infections and produce new blood cells gets compromised.
Several factors play a role in blood cancer development. Some of the blood cancer causes include:
-
Genetic mutations
-
Exposure to certain environmental factors
-
Immune system dysfunction
The exact cause of this disease is still not evident. However, several genetic research studies have shed light on the underlying mechanisms.
There are a few warning signs and symptoms of blood cancer. It includes:
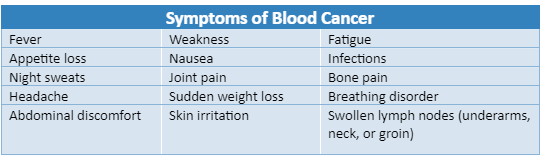
If these blood cancer symptoms persist longer, consult an expert cancer specialist to detect the issue as early as possible.
Types of Blood Cancer
There are three main blood cancer types. These categories are based on the affected blood cells and tissues.
Leukaemia
Originating in the blood cells in the bone marrow, it occurs due to increased white blood cell levels. It restricts the bone marrow’s ability to produce red blood cells and platelets.
-
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): It affects the lymphoid cells. ALL is more prevalent in children, but older adults may also develop this cancer.
-
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): It is the most common type of leukaemia. It causes abnormal growth of the myeloid cells. AML results in the formation of red and white blood cells and platelets. There are several risk factors involved with this type. It includes old age, male gender, industrial chemical exposure, smoking, and history of cancer diseases and their treatment. It usually progresses more aggressively.
-
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): It progresses slowly and affects a specific white blood cell type (lymphocytes). This issue is more common in older adults.
-
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): It overproduces mature myeloid cells. Usually, genetic abnormalities may result in this type. It is more common in adults.
Lymphoma
It affects the lymphatic system. Being a part of our immunity system, it filters and circulates lymph fluid throughout our body.
-
Hodgkin Lymphoma: If one has a history of infection with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), the chances of this disease get higher. The presence of an abnormal cell (Reed-Sternberg cells) characterises this lymphoma type. Males, older adults, history of Hodgkin lymphoma, and weak immunity are more at risk.
-
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL): It includes a diverse group of lymphomas not featuring Reed-Sternberg cells. It can occur at any age. Exposure to industrial chemicals and radiation, chemotherapy, history of autoimmune disorders, and weak immune system are more susceptible.
Myeloma
Myeloma is a plasma cell tumour that primarily affects the plasma cells in the bone marrow. Plasma cells are white blood cells that make antibodies to protect us from infections. In myeloma, these cells grow abnormally and multiply, affecting the production of other blood cells. It compromises the body’s ability to fight infections.
Multiple myeloma is the most common type of myeloma. Other types include Solitary plasmacytoma and Extramedullary plasmacytoma. Older adults, males, and obese people have a higher risk of developing myeloma.
The specific type of blood cancer can only be determined after proper diagnosis. If you are doubtful, discuss your health concern with a top oncologist in Bangalore
Treatment of Blood Cancer
The treatment method depends on the specific type of blood cancer and one’s health condition. Here is a brief idea about the available options.
Chemotherapy
This approach uses powerful drugs to either kill cancer cells or impede their growth. They circulate throughout the bloodstream. It targets cancer cells in the blood and other body parts, too. Chemotherapy may have adverse effects on healthy cells. It can cause nausea, fatigue, and hair loss.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy, also called Radiotherapy, uses high-energy rays such as X-rays or protons to target and destroy cancer cells. This approach usually focuses on the specific areas where cancer cells are present. It can be used as the primary treatment or in combination with other options. It may cause fatigue and skin irritation.
Stem Cell Transplant
This method is also known as bone marrow transplant. It involves replacing damaged or cancerous bone marrow with healthy stem cells. This procedure aims to restore the production of normal blood cells. The source of these healthy stem cells can either be the patient (autologous transplant) or a donor (allogeneic transplant). When high doses of chemotherapy or radiation become necessary, this approach becomes critical.
Immunotherapy
This method uses the body's immunity to recognise and eliminate cancer cells. It may involve using immune checkpoint inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, or adoptive cell therapy. Immunotherapy aims to enhance the body's natural defences against cancer. It is considered a targeted and less damaging alternative to traditional treatments.
Targeted Therapy
As the name implies, this treatment uses drugs designed to target cancer cells specifically. It also minimises harm to normal cells. They interfere with specific molecules that contribute to cancer cell growth. This approach is particularly useful if genetic mutations or abnormalities cause blood cancer.
Supportive Care
It is vital to improve the patient’s quality of life throughout the treatment process. It involves managing symptoms and side effects. The measures may include pain management, nutritional support, and psychosocial interventions. Blood cancer may affect the patients emotionally. So, it is crucial to keep a check on their mental health.
With advancements in medical research and technology, the treatment options for blood cancer have increased. It is getting better day by day. Despite this condition, cancer patients require huge support from their family and friends at every step of their journey.
For early diagnosis and accurate blood cancer treatment plans, visit Manipal Hospital Whitefield, Bangalore, and consult one of our best oncologists in Whitefield.
FAQ's
There are still no evident specific preventive measures. However, following a healthy lifestyle and avoiding smoking and exposure to harmful chemicals can help you avoid known risk factors for blood cancer.
People with inherited genetic mutations are more prone to develop certain blood cancers such as Leukaemia. However, not everyone with genetic features will develop the condition.
No, the treatment approach will vary depending on your health condition, cancer type and stage, and age.



















 6 Min Read
6 Min Read












